For Each Of The Following Forbidden Decays Determine Which Conservation Law Is Violated Beginar

Solved The Following Decays Are Forbidden Determine A Conservation (a) violates the conservation of muon number, (b) violates the conservation of lepton number, (c) violates the conservation of strangeness, (d) violates the conservation of baryon number and (e) violates the conservation of charge. Use baryon number, lepton number, and strangeness conservation to determine if particle reactions or decays occur. conservation laws are critical to an understanding of particle physics. strong evidence exists that energy, momentum, and angular momentum are all conserved in all particle interactions. the annihilation of an electron and positron.

Solved 1 Each Of The Following Decays Is Forbidden For Chegg Allowed and forbidden particle decays. discrete particles tend to be unstable and to decay into two or more particles of lesser mass unless they are forbidden to do so by some principle or conservation law. this tendency is sometimes referred to as the totalitarian principle. it is instructive to look at some allowed and forbidden decays and to. This process conserves charge, energy, and momentum. however, it does not occur because it violates the law of baryon number conservation. this law requires that the total baryon number of a reaction is the same before and after the reaction occurs. to determine the total baryon number, every elementary particle is assigned a baryon number b. 1. each of the following decays is forbidden. for each process, identify the conservation law(s) that is (are) violated. check b, lc, lu, l., and s. (2 pts each) a) u → e y b) np e ve c) aº → p ° d) p et tº e) sº ºn tº. Step 1. the charge on left side of equation is − 1 and the total charge on right side of equation is also − 1 2. each of the following decays is forbidden. for each, identify the conservation law (s) that is (are) not obeyed. (a) μ− →e− γ (b) Λ0 →p π0 (c) p→π π0 (d) Ξ0 →n π0.
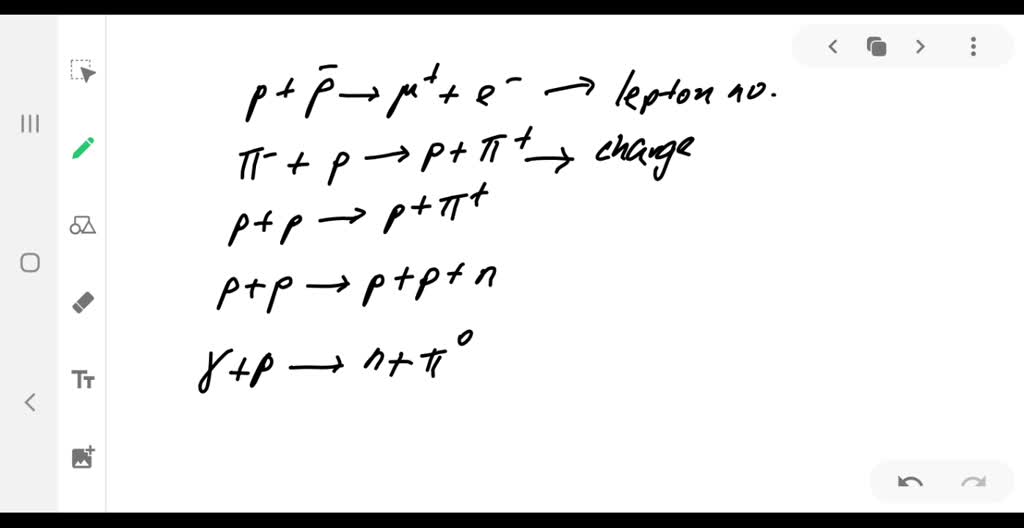
Solved Each Of The Following Reactions Is Forbidden Determine A 1. each of the following decays is forbidden. for each process, identify the conservation law(s) that is (are) violated. check b, lc, lu, l., and s. (2 pts each) a) u → e y b) np e ve c) aº → p ° d) p et tº e) sº ºn tº. Step 1. the charge on left side of equation is − 1 and the total charge on right side of equation is also − 1 2. each of the following decays is forbidden. for each, identify the conservation law (s) that is (are) not obeyed. (a) μ− →e− γ (b) Λ0 →p π0 (c) p→π π0 (d) Ξ0 →n π0. Use baryon number, lepton number, and strangeness conservation to determine if particle reactions or decays occur. conservation laws are critical to an understanding of particle physics. strong evidence exists that energy, momentum, and angular momentum are all conserved in all particle interactions. the annihilation of an electron and positron. Mesons are formed from the following combinations of quarks (subscripts indicate color and a r = antired a r = antired): (d r, d − ar) (d r, d − ar), (s g, u − ag s g, u − ag), and (s r, s − ar s r, s − ar). (a) determine the charge and strangeness of each combination. (b) identify one or more mesons formed by each quark antiquark.

Comments are closed.