Food Chain With A Producer And 3 Consumers
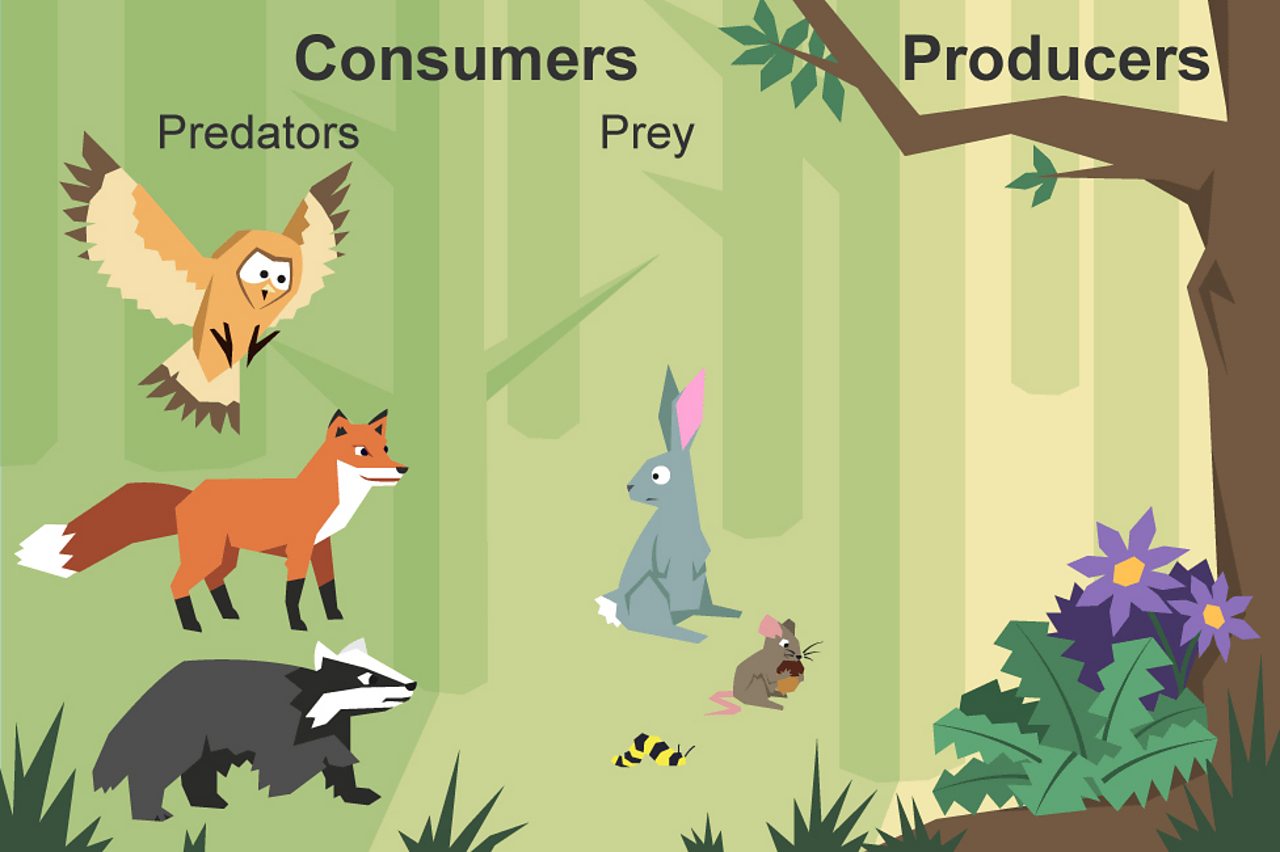
What Is A Food Chain Bbc Bitesize Examples of producers and consumers in science are all around the world. explore the different plant and animal examples of producers and consumers. As shown in the infographic below, a basic food chain is composed of producers, consumers, and decomposers. the 4 levels of the food chain consist of: producers: at the bottom of the food chain, plants are natural producers and provide food and nutrients to consumers. herbivores: herbivores (primary consumers) nourish plants and insects.
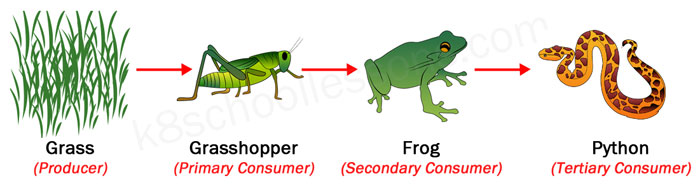
Producers And Consumers Food Chain 4th Grade Science A producer is an organism that makes its own food. most food chains start with a green plant, because plants make their own food by photosynthesis. a consumer is a living thing that eats other. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. Definition of food chain. a food chain shows energy pathways in ecosystems. each ecosystem on the planet has food chains of organisms ranging from producers to consumers. the producers are on the lowest level of the food chain, while the consumers that eat those producers are called primary consumers. higher level consumers who eat those. Trophic levels organisms in food chains are grouped into categories called trophic levels. roughly speaking, these levels are divided into producers (first trophic level), consumers (second, third, and fourth trophic levels), and decomposers. producers, also known as autotrophs, make their own food. they make up the first level of every food chain.

Food Chain And Food Webs Explained Definition of food chain. a food chain shows energy pathways in ecosystems. each ecosystem on the planet has food chains of organisms ranging from producers to consumers. the producers are on the lowest level of the food chain, while the consumers that eat those producers are called primary consumers. higher level consumers who eat those. Trophic levels organisms in food chains are grouped into categories called trophic levels. roughly speaking, these levels are divided into producers (first trophic level), consumers (second, third, and fourth trophic levels), and decomposers. producers, also known as autotrophs, make their own food. they make up the first level of every food chain. A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, non linear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics (figure 3). figure 3. this food web shows the interactions between organisms across trophic levels in the lake ontario ecosystem. Organisms in the food chain are divided into trophic levels or feeding levels. the four essential parts are the sun, primary producers, consumers, and decomposers. every food chain originates with the sun providing light and energy for plants to grow and ends with the decomposition of the animals.
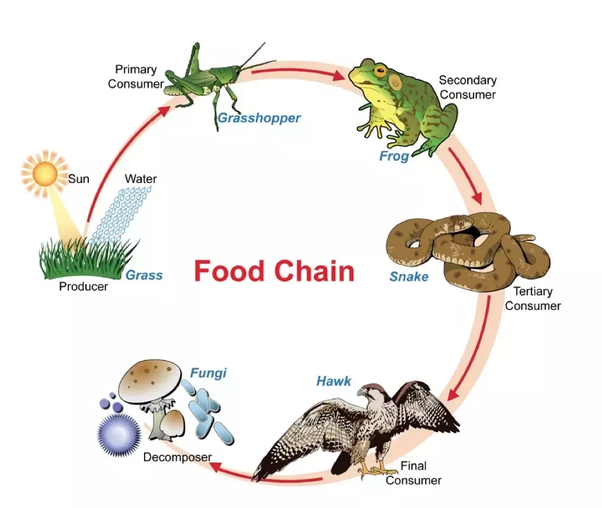
Food Chain Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, non linear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics (figure 3). figure 3. this food web shows the interactions between organisms across trophic levels in the lake ontario ecosystem. Organisms in the food chain are divided into trophic levels or feeding levels. the four essential parts are the sun, primary producers, consumers, and decomposers. every food chain originates with the sun providing light and energy for plants to grow and ends with the decomposition of the animals.
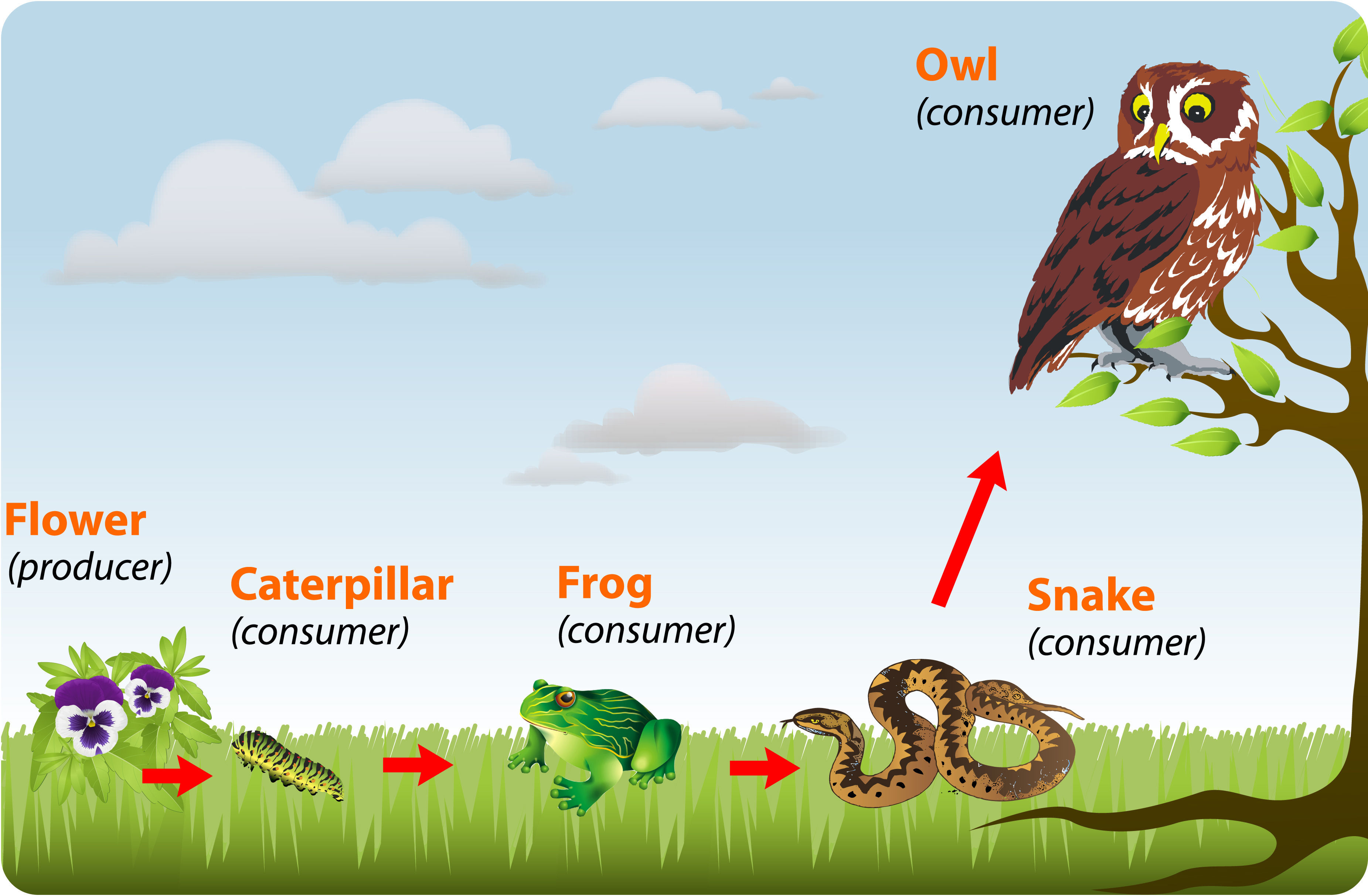
Food Chain In Terrestrial Ecosystem

Comments are closed.