Focal Vs Diffuse Gall Bladder Wall Thickening
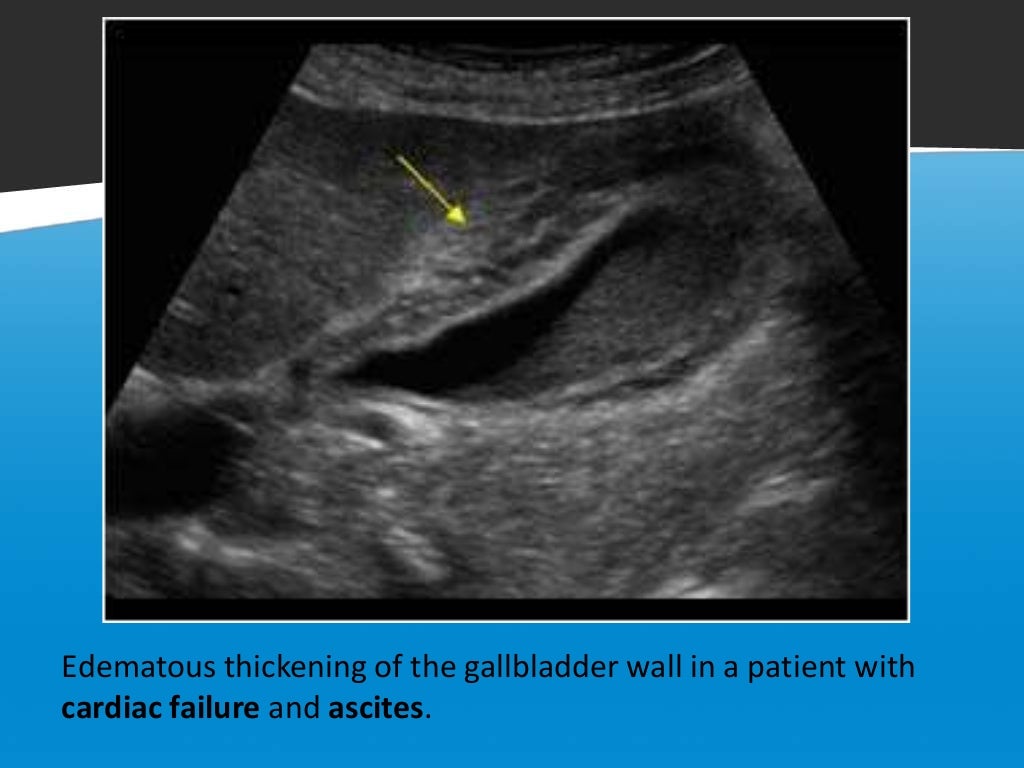
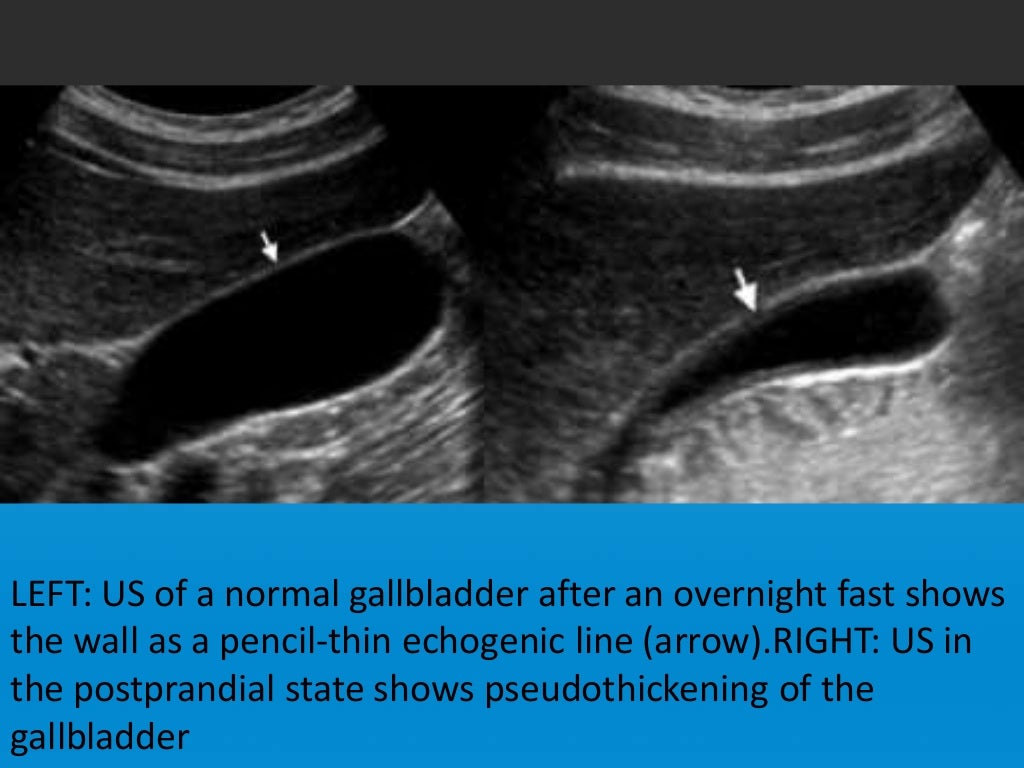
Focal Vs Diffuse Gall Bladder Wall Thickening Renal failure 11. gallbladder carcinoma. a minority present as focal or diffuse wall thickening (20 30%) 11,12. suspicious features include marked asymmetric wall thickening and irregularity 12. diffuse adenomyomatosis of the gallbladder. associated with classic comet tail artifact 11. associated with epithelial enhancement on ct 11. Gallbladder wall thickening can be caused by inflammatory, benign, and malignant etiologies. pseudothickening caused by the normal postprandial state of the contracted gallbladder is also extremely common 5. thus, for all non emergent exams, a fasting period of 6 12 hours (fewer or none in children) is advised to achieve maximal gallbladder.
Focal Vs Diffuse Gall Bladder Wall Thickening A, longitudinal ultrasound image of gallbladder shows shadowing gallstones (solid arrow) and diffuse wall thickening (3.5 mm) (calipers) with alternating hyperechoic and hypoechoic bands (dashed arrow). open in viewer. fig. 2b —acute cholecystitis with gallbladder necrosis in 40 year old woman. The thickening may be contained to one section of your gallbladder or spread throughout the gallbladder. thickening throughout the gallbladder is usually a sign of a noncancerous inflammatory. Diffuse gallbladder wall thickening can result from a broad spectrum of pathological conditions, including surgical and non surgical diseases. at times a definite imaging diagnosis may be impossible. in most cases however, the cause can be determined by correlation of the associated imaging findings with the clinical presentation. Gallbladder (gb) wall thickening is a frequent finding caused by a spectrum of conditions. it is observed in many extracholecystic as well as intrinsic gb conditions. gb wall thickening can either be diffuse or focal. diffuse wall thickening is a secondary occurrence in both extrinsic and intrinsic pathologies of gb, whereas, focal wall.

Comments are closed.