Figure 1 From Association Of Urinary Tract Infection And

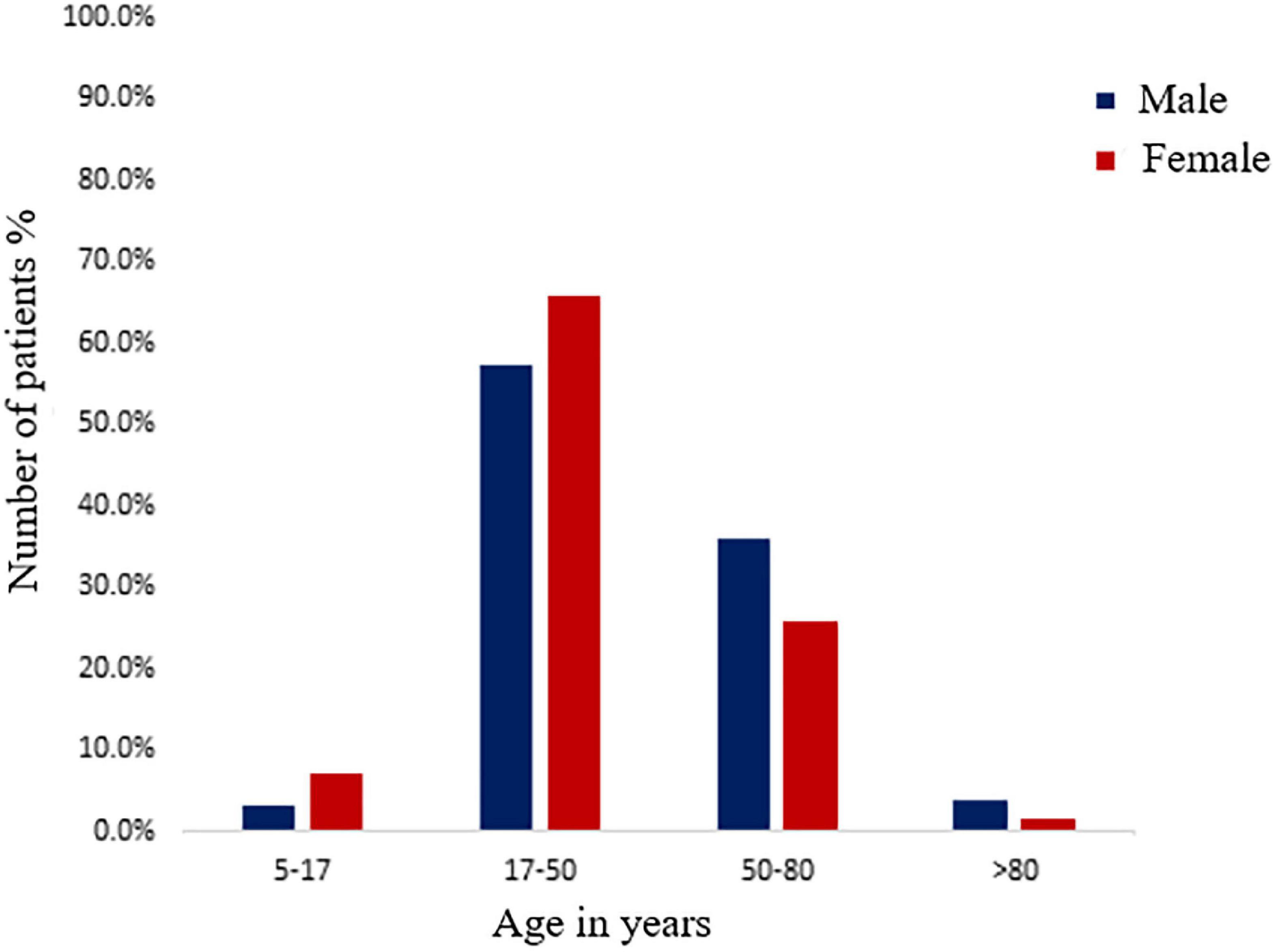
Figure 1 From Urinary Tract Infection And Asymptomatic Bacteriuria In Introduction. urinary tract infections (utis) are common in the elderly, and cover a range of conditions from asymptomatic bacteriuria through to uti associated sepsis requiring hospitalization.1,2 urinary growth of bacteria in the absence of urinary tract symptoms (i.e. asymptomatic bacteriuria) is most common and represents a commensal colonization.3 asymptomatic bacteriuria has a prevalence. Urinary tract infections (utis) are the fifth most common type of healthcare associated infection, with an estimated 62,700 utis in acute care hospitals in 2015. utis additionally account for more than 9.5% of infections reported by acute care hospitals 1. virtually, all healthcare associated utis are caused by instrumentation of the urinary tract.

Figure 1 From Risk Factors And Predisposing Conditions For Urinary Background. over the past few decades, our ability to diagnose, treat, and manage recurrent urinary tract infection (ruti) long term has evolved due to additional insights into the pathophysiology of ruti, a new appreciation for the adverse effects of repetitive antimicrobial therapy (“collateral damage”), rising rates of bacterial antimicrobial resistance, and better reporting of the. Figure 1. current and future approaches in the prevention and treatment of catheter associated urinary tract infections. schematic depiction of an indwelling urinary catheter (yellow) with its proximal end within the urinary bladder (orange). the balloon is shown in blue and the catheter drainage hole in black. Urinary tract infection (uti) is common in older adults, mainly due to several age related risk factors. symptoms of uti are atypical in the elderly population, like hypotension, tachycardia, urinary incontinence, poor appetite, drowsiness, frequent falls, and delirium. uti manifests more commonly and specifically for this age group as delirium. Figure 1. uncomplicated and complicated urinary tract infection (uti) defined by the european association of urology using orenuc. "urinary tract infections in the elderly: a review of disease characteristics and current treatment options".

Figure 1 From Management Of Urinary Tract Infections Problems And Urinary tract infection (uti) is common in older adults, mainly due to several age related risk factors. symptoms of uti are atypical in the elderly population, like hypotension, tachycardia, urinary incontinence, poor appetite, drowsiness, frequent falls, and delirium. uti manifests more commonly and specifically for this age group as delirium. Figure 1. uncomplicated and complicated urinary tract infection (uti) defined by the european association of urology using orenuc. "urinary tract infections in the elderly: a review of disease characteristics and current treatment options". Purpose: this document seeks to establish guidance for the evaluation and management of women with recurrent urinary tract infections (ruti) to prevent inappropriate use of antibiotics, decrease the risk of antibiotic resistance, reduce adverse effects of antibiotic use, provide guidance on antibiotic and non antibiotic strategies for prevention, and improve clinical outcomes and quality of. Acute uncomplicated cystitis is one of the most common infectious diseases in women, with a lifetime risk of greater than 50%. 1 approximately 27% of women with their first episode of cystitis will have at least 1 recurrence within 6 months, 2 and among women with previous urinary tract infection (uti), 44% to 70% will have a recurrence within.
Frontiers Bacterial Profile And Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern Of Purpose: this document seeks to establish guidance for the evaluation and management of women with recurrent urinary tract infections (ruti) to prevent inappropriate use of antibiotics, decrease the risk of antibiotic resistance, reduce adverse effects of antibiotic use, provide guidance on antibiotic and non antibiotic strategies for prevention, and improve clinical outcomes and quality of. Acute uncomplicated cystitis is one of the most common infectious diseases in women, with a lifetime risk of greater than 50%. 1 approximately 27% of women with their first episode of cystitis will have at least 1 recurrence within 6 months, 2 and among women with previous urinary tract infection (uti), 44% to 70% will have a recurrence within.
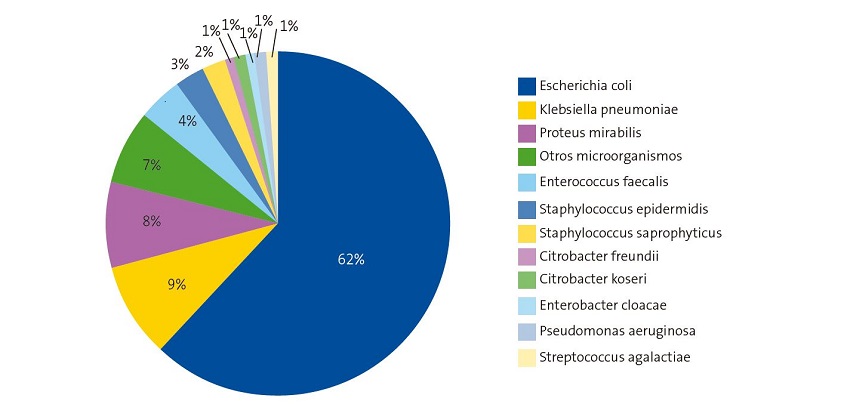
Revista De Pediatrг A De Atenciгіn Primaria Urinary Tract Infections

Comments are closed.