Febrile Baby Urinary Tract Infection Uti Pediatrics Lecturio

Febrile Baby Urinary Tract Infection Uti вђ Pediatrics Lecturio Sign up here and try our free content: lectur.io freecontentyt if you’re an medical educator or faculty member, visit: lectur.io medytb2u t. After 1st febrile uti uti urinary tract infections (utis) represent a wide spectrum of diseases, from self limiting simple cystitis to severe pyelonephritis that can result in sepsis and death. urinary tract infections are most commonly caused by escherichia coli, but may also be caused by other bacteria and fungi.
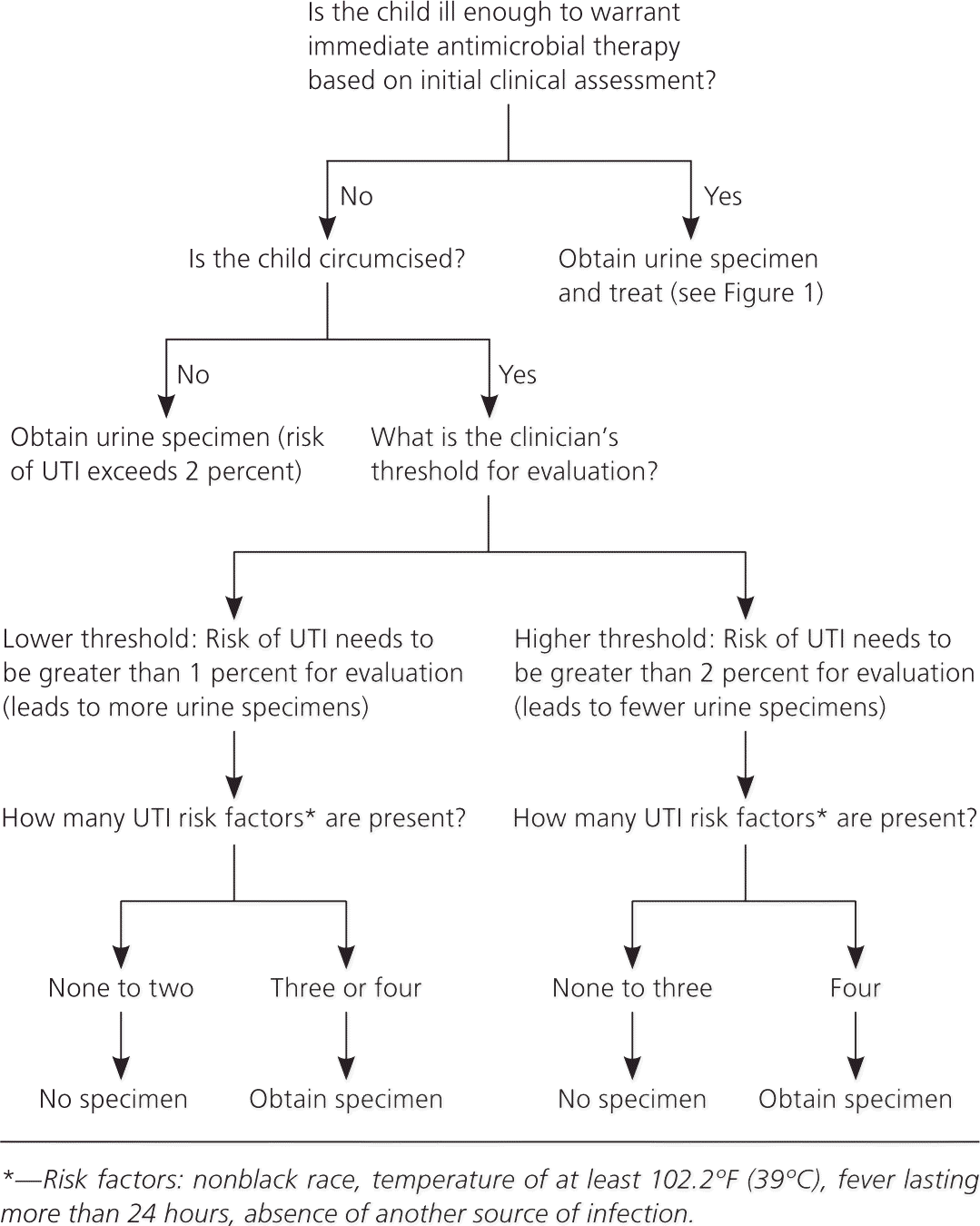
Revised Aap Guideline On Uti In Febrile Infants And Young Children Aafp Table: criteria for the management of the febrile baby (28 days–56 days old) rochester, ny philadelphia, pa boston, ma; ultrasonography, urine culture urine culture urinary tract infections (utis), cbc, blood culture: yes: yes: yes: spinal tap: if abnormal testing: yes: yes. Urinary tract infections (utis) represent a wide spectrum of diseases, from self limiting simple cystitis to severe pyelonephritis that can result in sepsis and death. urinary tract infections are most commonly caused by escherichia coli, but may also be caused by other bacteria and fungi. Recent studies have resulted in major changes in the management of urinary tract infections (utis) in children. the present statement focuses on the diagnosis and management of infants and children >2 months of age with an acute uti and no known underlying urinary tract pathology or risk factors for a neurogenic bladder. uti should be ruled out in preverbal children with unexplained fever and. A state of the art review of current literature on uti in children, with a particular focus on its diagnosis and management by general pediatricians.urinary tract infection (uti) is common in children, and girls are at a significantly higher risk, as compared to boys, except in early infancy. most cases are caused by escherichia coli. collection of an uncontaminated urine specimen is essential.

Urinary Tract Infections In Infants And Children Walter Bushnell Recent studies have resulted in major changes in the management of urinary tract infections (utis) in children. the present statement focuses on the diagnosis and management of infants and children >2 months of age with an acute uti and no known underlying urinary tract pathology or risk factors for a neurogenic bladder. uti should be ruled out in preverbal children with unexplained fever and. A state of the art review of current literature on uti in children, with a particular focus on its diagnosis and management by general pediatricians.urinary tract infection (uti) is common in children, and girls are at a significantly higher risk, as compared to boys, except in early infancy. most cases are caused by escherichia coli. collection of an uncontaminated urine specimen is essential. Urinary tract infection: clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of the initial uti in febrile infants and children 2 to 24 months. pediatrics. 2011;128(3):595 610. Objectives:. the diagnosis and management of urinary tract infections (utis) in young children are clinically challenging. this report was developed to inform the revised, evidence based, clinical guideline regarding the diagnosis and management of initial utis in febrile infants and young children, 2 to 24 months of age, from the american academy of pediatrics subcommittee on urinary tract.

Comments are closed.