Exponential Growth And Decay Math
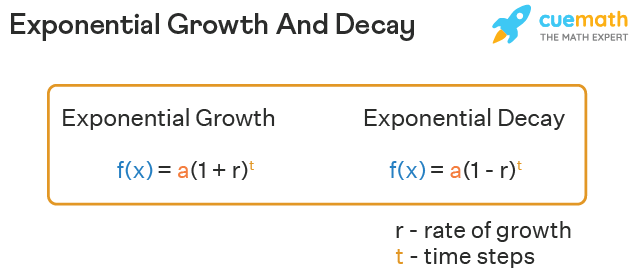
Exponential Growth And Decay Definition Formula Examples Growth and decay. but sometimes things can grow (or the opposite: decay) exponentially, at least for a while. so we have a generally useful formula: y (t) = a × e kt. where y (t) = value at time "t". a = value at the start. k = rate of growth (when >0) or decay (when <0) t = time. example: 2 months ago you had 3 mice, you now have 18. Key concepts. exponential growth and exponential decay are two of the most common applications of exponential functions. systems that exhibit exponential growth follow a model of the form y = y0ekt. in exponential growth, the rate of growth is proportional to the quantity present. in other words, y′ = ky.

Exponential Growth Decay Formula Function Graphs Lesson Learn how to use exponential functions to model real world scenarios, such as population growth, radioactive decay, and compound interest. compare and contrast exponential and linear growth with khan academy's interactive exercises. Compound internet, decpreciation, growth of virus, spoiling of perishable foods, are some of the real life examples which need to be calculated using a math formula. the exponential growth and decay gives the required needed calculations using the formulas f (x) = a (1 r) t, and f (x) = a (1 r) t. Likewise, if a > 0, then the more general exponential function \(ab^t\) also exhibits exponential decay, since the graph of \(ab^t\) is just a vertical scaling of the graph of bt. however, the exponential decay function in formula (9) appears to be different. we will show below that the function \(p {0}e^{−rt}\) can in fact be written in the. A graph showing exponential decay. the equation is y=3e−2x y = 3 e − 2 x. exponential growth and decay often involve very large or very small numbers. to describe these numbers, we often use orders of magnitude. the order of magnitude is the power of ten when the number is expressed in scientific notation with one digit to the left of the.
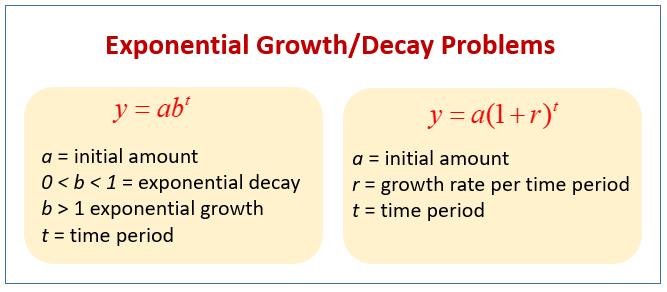
Exponential Growth And Decay Explained Likewise, if a > 0, then the more general exponential function \(ab^t\) also exhibits exponential decay, since the graph of \(ab^t\) is just a vertical scaling of the graph of bt. however, the exponential decay function in formula (9) appears to be different. we will show below that the function \(p {0}e^{−rt}\) can in fact be written in the. A graph showing exponential decay. the equation is y=3e−2x y = 3 e − 2 x. exponential growth and decay often involve very large or very small numbers. to describe these numbers, we often use orders of magnitude. the order of magnitude is the power of ten when the number is expressed in scientific notation with one digit to the left of the. Exponential decay: y = a (1 r) x. remember that our original exponential formula was y = a (b) x. you will notice that in these new growth and decay functions, the b value (growth factor) has been replaced either by (1 r) or by (1 r). the growth "rate" (r) is determined as b = 1 r. the decay "rate" (r) is determined as b = 1 r. Moreover, if b = 1 r, we call r the growth rate. whenever b> 1, we often say that the function f is exhibiting “exponential growth”, wherease if 0 <b <1, we say f exhibits “exponential decay”. we explore the properties of functions of form f(t) = abt further in activity 3.1.2.
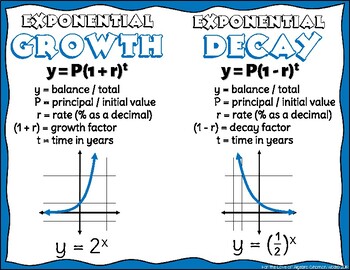
Exponential Growth Decay Poster Gse Algebra 1 By For The Love Of Exponential decay: y = a (1 r) x. remember that our original exponential formula was y = a (b) x. you will notice that in these new growth and decay functions, the b value (growth factor) has been replaced either by (1 r) or by (1 r). the growth "rate" (r) is determined as b = 1 r. the decay "rate" (r) is determined as b = 1 r. Moreover, if b = 1 r, we call r the growth rate. whenever b> 1, we often say that the function f is exhibiting “exponential growth”, wherease if 0 <b <1, we say f exhibits “exponential decay”. we explore the properties of functions of form f(t) = abt further in activity 3.1.2.

Exponential Growth And Decay Math

Comments are closed.