Emory Edu Bladder Transverse Sediment Hemorrhage 817г 549 Ultrasound

Emory Edu Bladder Transverse Sediment Hemorrhage 817г 5 Emory university school of medicine bladder transverse sediment hemorrhage; ultrasound ultrasound education faculty. This clip was reported as part of a "negative" fast. the echogenic debris within this fluid filled structure is actually mucin from a previously undiagnosed ovarian tumor in a young woman. no clip of the bladder was recorded. emory em doctors made note of this recently when they noted a similar structure in the pelvis on a transverse view.
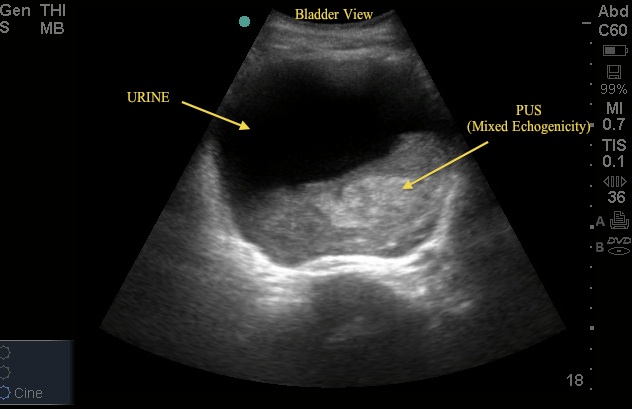
Ultrasound Images Renal Emory School Of Medicine Renal and bladder ultrasound (rbus) is recommended in the evaluation of children after an initial, febrile urinary tract infection (uti) . as a part of rbus, the american college of radiology recommends that the bladder walls and lumen be evaluated [2,3]. findings may include stones, masses, or mobile debris in the lumen (fig. 1). bladder. Presence or absence of bladder debris was reported by the original reading radiologist on nearly all ultrasound reports, including a subjective determination of the bladder debris severity (mild, moderate, severe, or no debris; see fig. 1). a representative sample of 10% of the ultrasound images were reviewed by the authors to confirm accuracy. A pelvic diameter of 7 mm is the upper limit of normal for neonates and in older children it is 10 mm (measured transversely) 1, 2 6. urothelial thickening can be seen in urinary tract infection or reflux 7. if a renal tumour is suspected, this should include the ivc to assess for tumour thrombus. Step 1: bladder ultrasound – longitudinal view. place the transducer with the indicator pointing towards the patient’s head in the patient’s midline, right above the pubic symphysis. rock the probe so that it points down towards the pelvic cavity. bladder ultrasound – longitudinal view.
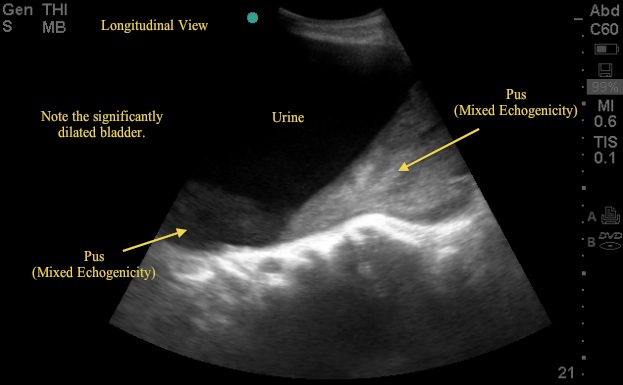
Ultrasound Images Renal Emory School Of Medicine A pelvic diameter of 7 mm is the upper limit of normal for neonates and in older children it is 10 mm (measured transversely) 1, 2 6. urothelial thickening can be seen in urinary tract infection or reflux 7. if a renal tumour is suspected, this should include the ivc to assess for tumour thrombus. Step 1: bladder ultrasound – longitudinal view. place the transducer with the indicator pointing towards the patient’s head in the patient’s midline, right above the pubic symphysis. rock the probe so that it points down towards the pelvic cavity. bladder ultrasound – longitudinal view. The most common indication for point of care ultrasound (poc us) of the urinary tract in the emergency department (ed) is flank pain, responsible for approximately 2 million ed visits in the united states annually. about 20% of patients presenting with flank pain have nephrolithiasis.[1] while computed tomography (ct) imaging is the gold standard for diagnosing urinary tract stones, poc us is. The bladder is a muscular sac that receives urine from your kidneys, stretching to hold the fluid until you release it during urination. bladder control, or your ability to control these muscles.
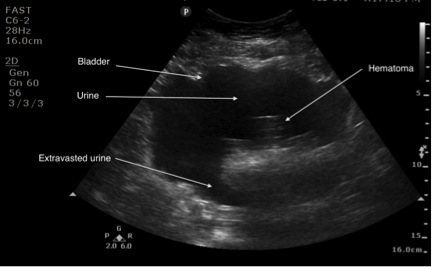
Case Of The Exploding Bladder Emory School Of Medicine The most common indication for point of care ultrasound (poc us) of the urinary tract in the emergency department (ed) is flank pain, responsible for approximately 2 million ed visits in the united states annually. about 20% of patients presenting with flank pain have nephrolithiasis.[1] while computed tomography (ct) imaging is the gold standard for diagnosing urinary tract stones, poc us is. The bladder is a muscular sac that receives urine from your kidneys, stretching to hold the fluid until you release it during urination. bladder control, or your ability to control these muscles.

Comments are closed.