Elementary Particles Gate Physics Problems And Solutions Allowed Forbidden Reaction

Elementary Particles Gate Physics Problems And Solutions Allo Hello friends,once again i am here to help you out in your online study. subscribe our channel. Problem 4 draw one forth order diagram for each of the reactions a) g e !g e , b) e e !e e c)and the two forth order diagrams for e m !ne n¯m. problem 5 for total centre of mass energies up to a fre gev, the cross section for the reaction nm e ! m nm is given by s = g2 fe 2 p in natural units, where gf is the fermi coupling constant. what.
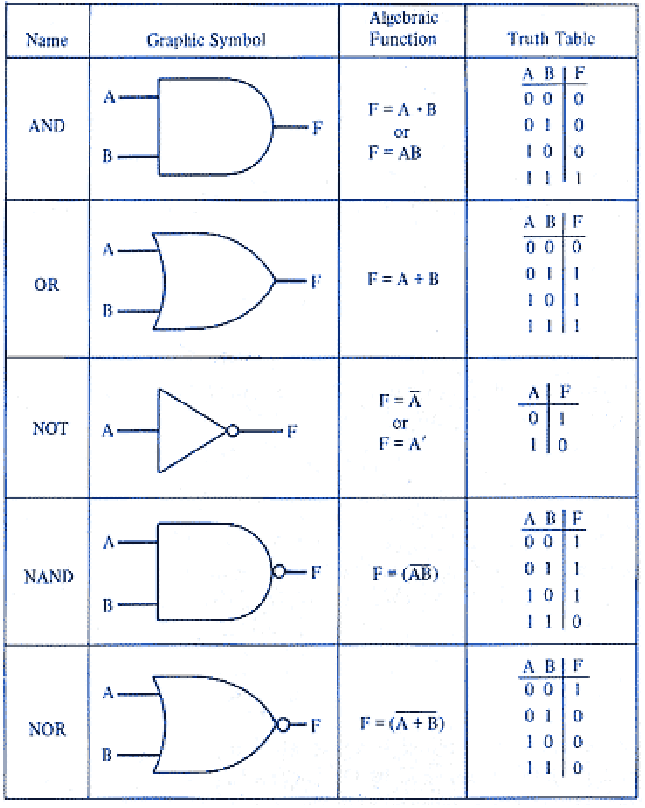
Logic Gates Exercises on elementary particles|solutions 1. forbidden reactions (a) p p! e : this reaction is forbidden by conservation of electron and muon family numbers. (b) ˇ p!p ˇ : this reaction is forbidden by conservation of electric charge. (c) p p!p ˇ : this reaction is forbidden by conservation of quark number. Q21. a nucleus x undergoes a first forbidden decay to nucleusy. if the angular momentum i and parity p, denoted by i p as 2 7 for x, which of the following is a possible i p value fory? (a) 2 1 (b) 2 1 (c) 2 3 (d) 2 3 ans: (c) solution: for first forbidden decay; i 0,1or 2 and parity does change. gate 2015 q22. Hence, this is also an allowed transition. altogether, this transition is allowed by conservation angular momentum, parity, and charge conjugation. (c) 13s 1 → 21p1 the 21p 1 state has charge conjugation c =(−1)1 0 = −1, so this transition is forbidden via single photon absorption by charge conjugation symmetry. This law requires that the total baryon number of a reaction is the same before and after the reaction occurs. to determine the total baryon number, every elementary particle is assigned a baryon number b. the baryon number has the value b = 1 b = 1 for baryons, –1 for antibaryons, and 0 for all other particles.
Particle Physics вђ Department Of Physics Hence, this is also an allowed transition. altogether, this transition is allowed by conservation angular momentum, parity, and charge conjugation. (c) 13s 1 → 21p1 the 21p 1 state has charge conjugation c =(−1)1 0 = −1, so this transition is forbidden via single photon absorption by charge conjugation symmetry. This law requires that the total baryon number of a reaction is the same before and after the reaction occurs. to determine the total baryon number, every elementary particle is assigned a baryon number b. the baryon number has the value b = 1 b = 1 for baryons, –1 for antibaryons, and 0 for all other particles. 6 1 historical introduction to the elementary particles problem 1.15 uu c¯ u u¯ c c¯ c¯ ud c¯ s d¯ c¯ du c¯ d¯ sc¯ dd¯ 3 have c = 1 3 have c = −1 us¯ su¯ ds¯ sd¯ ss¯ 10 have c = 0 (including cc¯) problem 1.16 qq¯ meson mass year uu¯ π0 (*) 134.98 1950 ud¯ π 139.57 1947 dd¯ π0 (*) 134.98 1950 u¯s k 493.68 1949 ds. Since the net baryon numbers of the reactants and products are equal, this reaction is allowed on the basis of the baryon number conservation law. for reaction (b), the net baryon number of the reactants is 1 (−1) = 0 1 (−1) = 0 and the net baryon number of the proposed products is 1 1 (−1) = 1. 1 1 (−1) = 1.

Comments are closed.