Echogenic Ultrasound

Intraabdominal Fetal Echogenic Masses A Practical Guide To Diagnosis Echogenic can describe normal tissue or organs. the term can also be used to describe abnormalities, such as a mass in an organ. we often use the term echogenic when comparing to other tissues. the radiologist interpreting the ultrasound may use the term echogenic but will often try to provide a more specific diagnosis to guide treatment. Echogenicity (sometimes as echogenecity) or echogeneity is the ability to bounce an echo, e.g. return the signal in medical ultrasound examinations. in other words, echogenicity is higher when the surface bouncing the sound echo reflects increased sound waves. tissues that have higher echogenicity are called "hyperechoic" and are usually.

Intraabdominal Fetal Echogenic Masses A Practical Guide To Diagnosis Abstract. ultrasound (us) use has rapidly entered the field of acute pain medicine and regional anesthesia and interventional pain medicine over the last decade, and it may even become the standard of practice. the advantages of us guidance over conventional techniques include the ability to both view the targeted structure and visualize, in. An echogenic kidney is one which whiter than usual on ultrasound. echogenic kidneys are not specific for a diagnosis but can indicate kidney problems. echogenic kidneys are determined by comparing them to adjacent organs like the liver and spleen. echogenic kidneys do not always indicate kidney disease and work up and further testing may be needed. Echogenicity: term used to describe the ability of a structure to reflect ultrasound waves and bounce (generate) echoes. the brightness of a structure appears on ultrasound screen depends on its surround structures. hyperechoic (more echogenic): structure appears brighter (more echogenic) on ultrasound than surrounding structures. Nodule echogenicity on gray scale ultrasound. (a) an 88 year old man with hyperechoic nodules (arrows) and hashimoto thyroiditis. (b) a 65 year old woman with an isoechoic nodule (calipers). (c) a 51 year old woman with nodules that are hypoechoic (curved arrow) and very hypoechoic (arrow).

Intraabdominal Fetal Echogenic Masses A Practical Guide To Diagnosis Echogenicity: term used to describe the ability of a structure to reflect ultrasound waves and bounce (generate) echoes. the brightness of a structure appears on ultrasound screen depends on its surround structures. hyperechoic (more echogenic): structure appears brighter (more echogenic) on ultrasound than surrounding structures. Nodule echogenicity on gray scale ultrasound. (a) an 88 year old man with hyperechoic nodules (arrows) and hashimoto thyroiditis. (b) a 65 year old woman with an isoechoic nodule (calipers). (c) a 51 year old woman with nodules that are hypoechoic (curved arrow) and very hypoechoic (arrow). Introduction. the echogenicity of the fetal bowel is assessed during second trimester obstetric ultrasound examinations because increased echogenicity is a marker for several fetal disorders, including some aneuploidies (most commonly trisomy 21, 13, and 18), cystic fibrosis (cf), some gastrointestinal abnormalities (eg, obstruction, atresia, perforation), growth restriction, and infection. A liver ultrasound can show signs of fat storage in your liver (steatotic liver disease), inflammation and swelling (hepatitis), and scar tissue (fibrosis or cirrhosis). these are the three main stages of chronic liver disease. the scan may also show liver lesions, abnormal spots or growths on your liver.
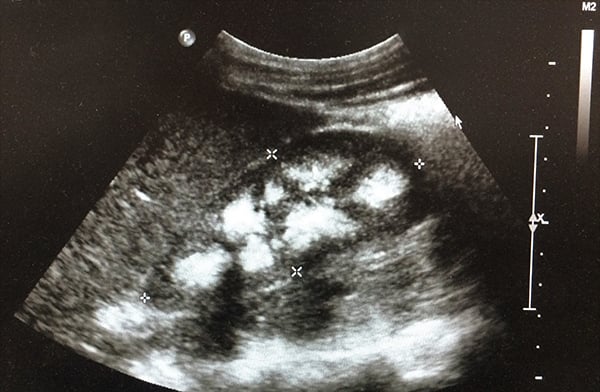
The Echogenic Kidney Emra Introduction. the echogenicity of the fetal bowel is assessed during second trimester obstetric ultrasound examinations because increased echogenicity is a marker for several fetal disorders, including some aneuploidies (most commonly trisomy 21, 13, and 18), cystic fibrosis (cf), some gastrointestinal abnormalities (eg, obstruction, atresia, perforation), growth restriction, and infection. A liver ultrasound can show signs of fat storage in your liver (steatotic liver disease), inflammation and swelling (hepatitis), and scar tissue (fibrosis or cirrhosis). these are the three main stages of chronic liver disease. the scan may also show liver lesions, abnormal spots or growths on your liver.
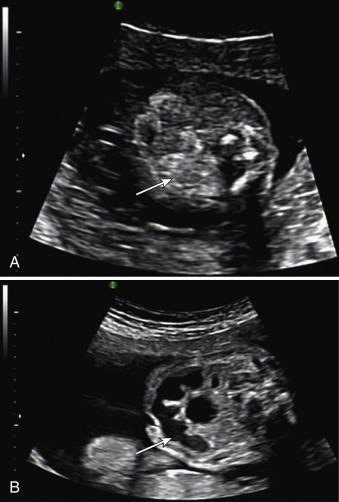
Echogenic Bowel Radiology Key

Comments are closed.