Ct Bladder Rupture From Large Prostate Case Discussion By A Radiologist

Ct Bladder Rupture From Large Prostate Case Discussion By A Radiologist This is a discussion of the findings and associated cross sectional anatomy in a patient with an extremely unusual case of an enlarged prostate, bladder outl. Discussion. a spontaneous urinary bladder rupture is an extremely rare pathological entity, with an incidence of 1: 126,000, and a mortality rate of around 50% [1, 4]. predisposing conditions are associated with weakening of the bladder wall and or increase in intra vesical pressure.

Bladder Rupture Ct Sumer S Radiology Blog The bladder is thick walled with a poorly defined anterior wall. there is a large volume of free fluid in the hepatorenal and splenorenal spaces. it is unclear as to why a trauma protocol (i.e. full body) ct was not acquired on presentation. instead, disparate investigations such as pelvic x ray and renal tract ultrasound were requested. Bladder injuries can be categorized as one of two types: intraperitoneal rupture. this involves the dome and causes urine to spill into the peritoneal cavity and surround the bowel loops. extraperitoneal rupture. this is usually anterior and the leaking urine is confined to the space surrounding the bladder. intraperitoneal bladder rupture. Extraperitoneal bladder rupture. the most common type of bladder injury, accounts for ~85% (range 80 90%) of cases. it is usually the result of pelvic fractures or penetrating trauma. cystography reveals a variable path of extravasated contrast material. treatment is with an indwelling urinary catheter. Although conventional radiographic cystography has been traditionally considered the reference standard in detecting bladder injuries, computed tomography (ct) cystography has become the initial imaging method of choice in the acute setting. ct cystography has been shown to provide comparable accuracy as conventional cystography, and can be easily performed in conjunction with trauma ct.
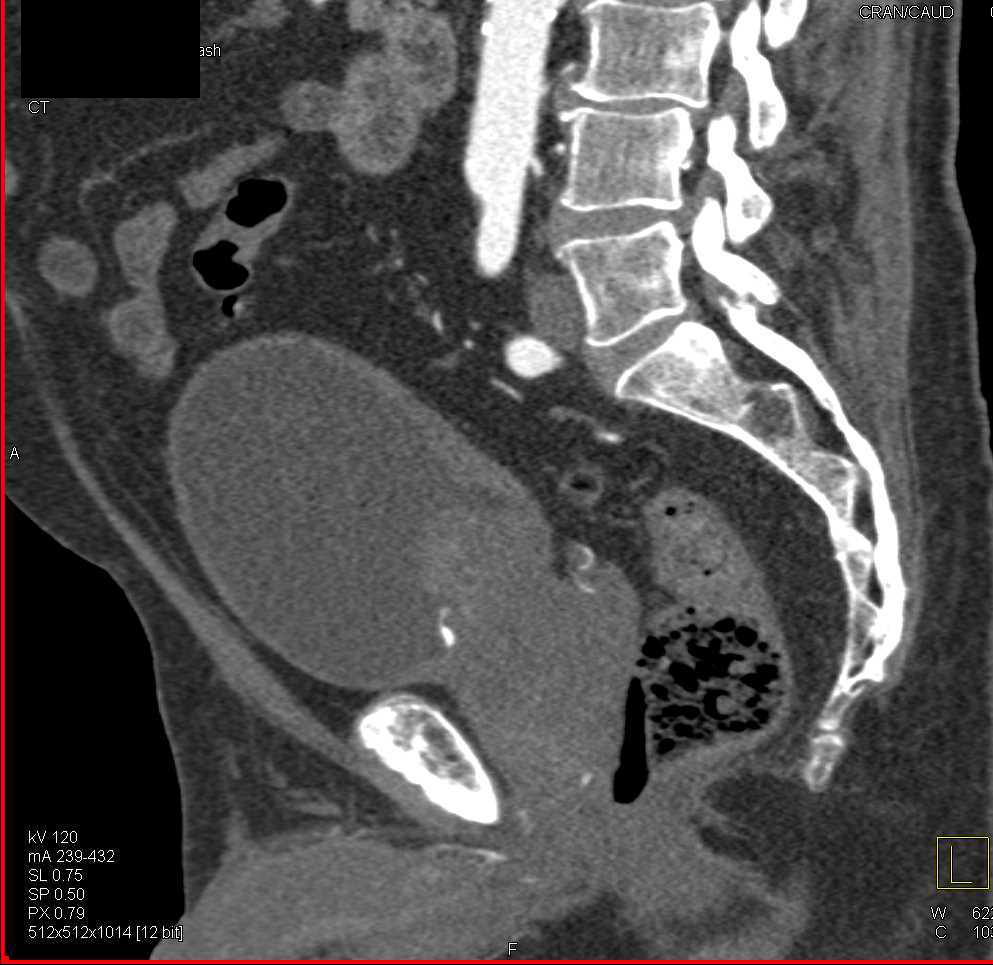
Enlarged Prostate With Bladder Outlet Obstruction Genitourinary Case Extraperitoneal bladder rupture. the most common type of bladder injury, accounts for ~85% (range 80 90%) of cases. it is usually the result of pelvic fractures or penetrating trauma. cystography reveals a variable path of extravasated contrast material. treatment is with an indwelling urinary catheter. Although conventional radiographic cystography has been traditionally considered the reference standard in detecting bladder injuries, computed tomography (ct) cystography has become the initial imaging method of choice in the acute setting. ct cystography has been shown to provide comparable accuracy as conventional cystography, and can be easily performed in conjunction with trauma ct. Case discussion. intraperitoneal bladder rupture can be differentiated from extraperitoneal bladder rupture, if contrast outlines loops of bowel. oblique images may also be helpful in differentiating the two, although localization using the normal positions of pelvic structures could be misleading in a postoperative pelvis. Ajr:204, june 2015. e mergent genitourinary conditions require timely diagnosis and treat ment to ensure a favorable clinical outcome and to prevent morbidity and mortality. ct is typically the imaging mo dality of choice for most emergent conditions of the genitourinary tract, and ultrasound is used less frequently.

Ct Cystography In The Evaluation Of Major Bladder Trauma Radiographics Case discussion. intraperitoneal bladder rupture can be differentiated from extraperitoneal bladder rupture, if contrast outlines loops of bowel. oblique images may also be helpful in differentiating the two, although localization using the normal positions of pelvic structures could be misleading in a postoperative pelvis. Ajr:204, june 2015. e mergent genitourinary conditions require timely diagnosis and treat ment to ensure a favorable clinical outcome and to prevent morbidity and mortality. ct is typically the imaging mo dality of choice for most emergent conditions of the genitourinary tract, and ultrasound is used less frequently.

Comments are closed.