Cross Section Of The Testis Epididymis And Tunica Vaginalis Vi Stock

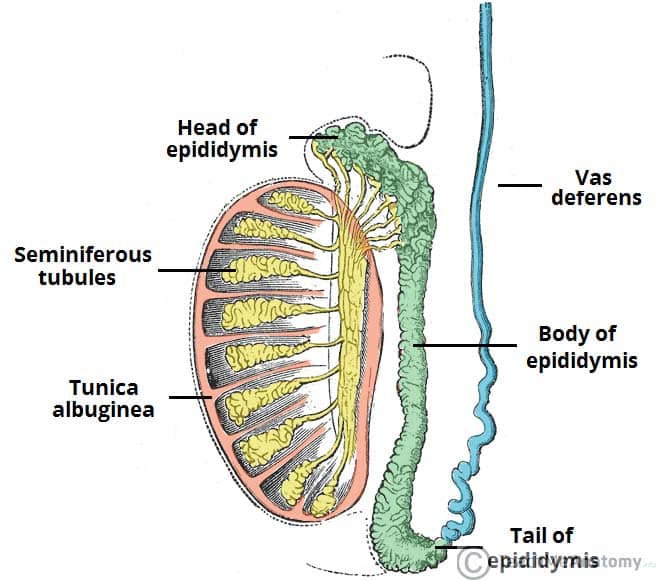
Cross Section Of The Testis Epididymis And Tunica Vaginalis Vi Stock Gross anatomy of the testis. the testes are paired organs in the scrotum, 4 × 3 × 2.5 cm, 20–25 ml volume. the testicles have a strong organ capsule (tunica albuginea testis). the testicular parenchyma is composed of 250–350 lobules, which drain through the mediastinum testis to the epididymis. the lobules are separated by connective. Ducts known as efferent tubules transport the sperm from the rete testes to the epididymis for storage and maturation. inside the scrotum, the testes are covered almost entirely by the tunica vaginalis, a closed sac of parietal peritoneal origin that contains a small amount of viscous fluid. this sac covers the anterior surface and sides of.
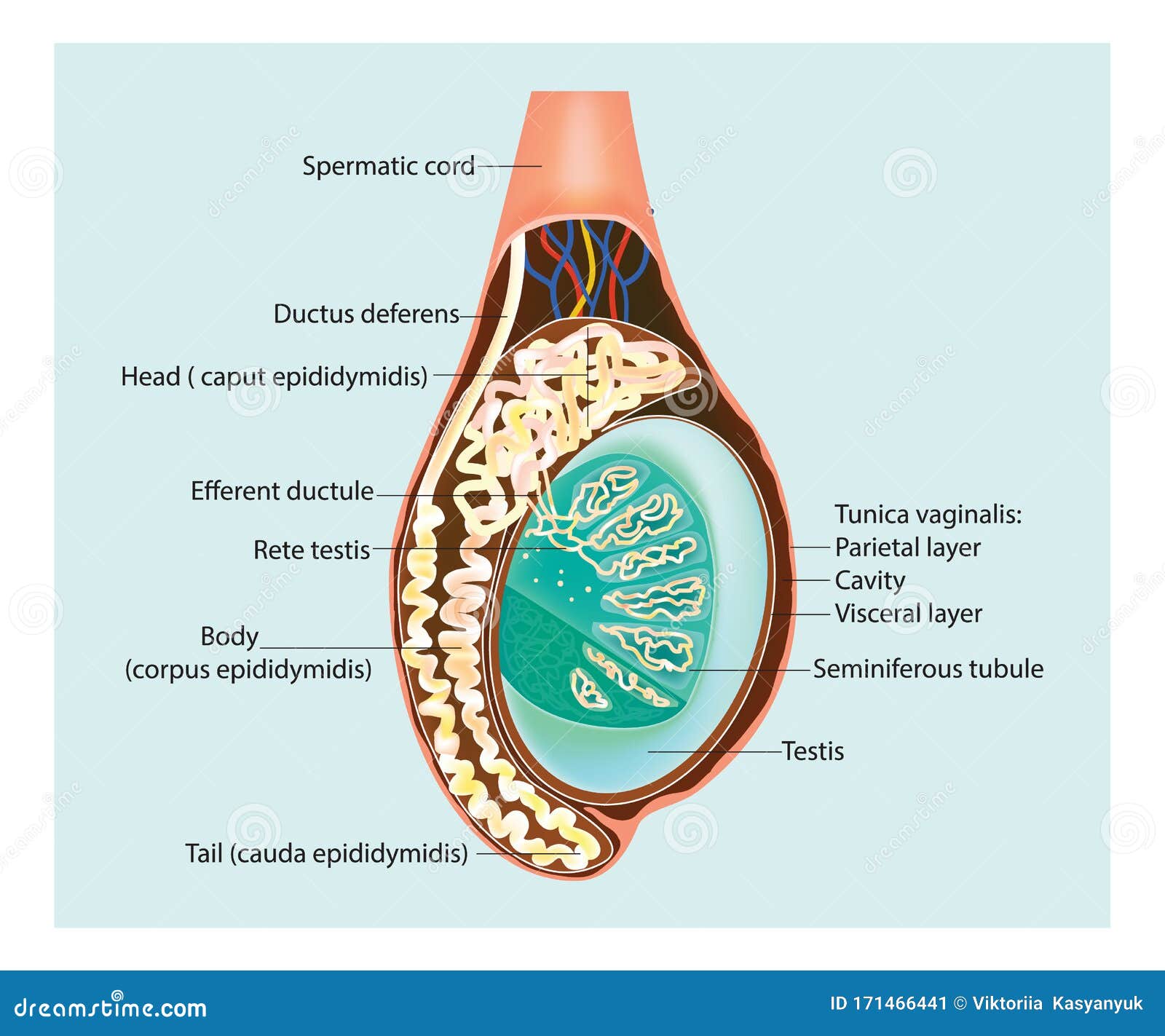
Illustration Of A Cross Section Of The Testis Epididymis Stock Vector 1 16. synonyms: none. the male reproductive system consists of the internal and external reproductive organs. the former consist of the testes, epididymis, spermatic cord, ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct and accessory glands, while the latter comprise the penis and the scrotum. the functions of this entire system are numerous, including. The testis is covered externally on its anterior and lateral aspects by a mesothelial layer of simple squamous epithelium termed the tunica vaginalis. (not visible in these photomicrographs.) deep to the tunica vaginalis you will find the tough connective tissue capsule of the testis, the tunica albuginea (figure 14 1). The tunica vaginalis is a pouch of [2] serous membrane [3] within the scrotum that lines the testis and epididymis (visceral layer of tunica vaginalis), and the inner surface of the scrotum (parietal layer of tunica vaginalis). it is the outermost of the three layers that constitute the capsule of the testis, with the tunica albuginea of testis. The descending testes stay at the opening of the vaginal process for about 10–12 weeks. at week 26–34 of gestation, testis and epididymis proceed into the vaginal process drawn by the gubernaculum. the distal part of the vaginal process directly surrounding testis and epididymis is called tunica vaginalis. this structure consists of two.
Epididymitis Clinical Features Management Teachmesurgery The tunica vaginalis is a pouch of [2] serous membrane [3] within the scrotum that lines the testis and epididymis (visceral layer of tunica vaginalis), and the inner surface of the scrotum (parietal layer of tunica vaginalis). it is the outermost of the three layers that constitute the capsule of the testis, with the tunica albuginea of testis. The descending testes stay at the opening of the vaginal process for about 10–12 weeks. at week 26–34 of gestation, testis and epididymis proceed into the vaginal process drawn by the gubernaculum. the distal part of the vaginal process directly surrounding testis and epididymis is called tunica vaginalis. this structure consists of two. On the posterolateral surface of the testis, this layer invests a slitlike recess between the body of the epididymis and the testis that is called the sinus of epididymis. [ 5 ] the parietal layer of tunica vaginalis is adjacent to the internal spermatic fascia, is more extensive, and extends superiorly into the distal part of the spermatic cord. The testis is both an exocrine (producing spermatozoa) and an endocrine (producing androgens) gland. this immature testis, cut in cross section, provides an overview of the testis proper, its enclosing tunics, and its location in the scrotum. also seen are the epididymis and the ductus deferens lying posterior to the testis. immature testis 10x.

The Testes And Epididymus Structure Vasculature Teachmeanatomy On the posterolateral surface of the testis, this layer invests a slitlike recess between the body of the epididymis and the testis that is called the sinus of epididymis. [ 5 ] the parietal layer of tunica vaginalis is adjacent to the internal spermatic fascia, is more extensive, and extends superiorly into the distal part of the spermatic cord. The testis is both an exocrine (producing spermatozoa) and an endocrine (producing androgens) gland. this immature testis, cut in cross section, provides an overview of the testis proper, its enclosing tunics, and its location in the scrotum. also seen are the epididymis and the ductus deferens lying posterior to the testis. immature testis 10x.

Testicle Epididymis Cross Section 3d Illustration Stock Illustration

Comments are closed.