Consumption And Saving Functions
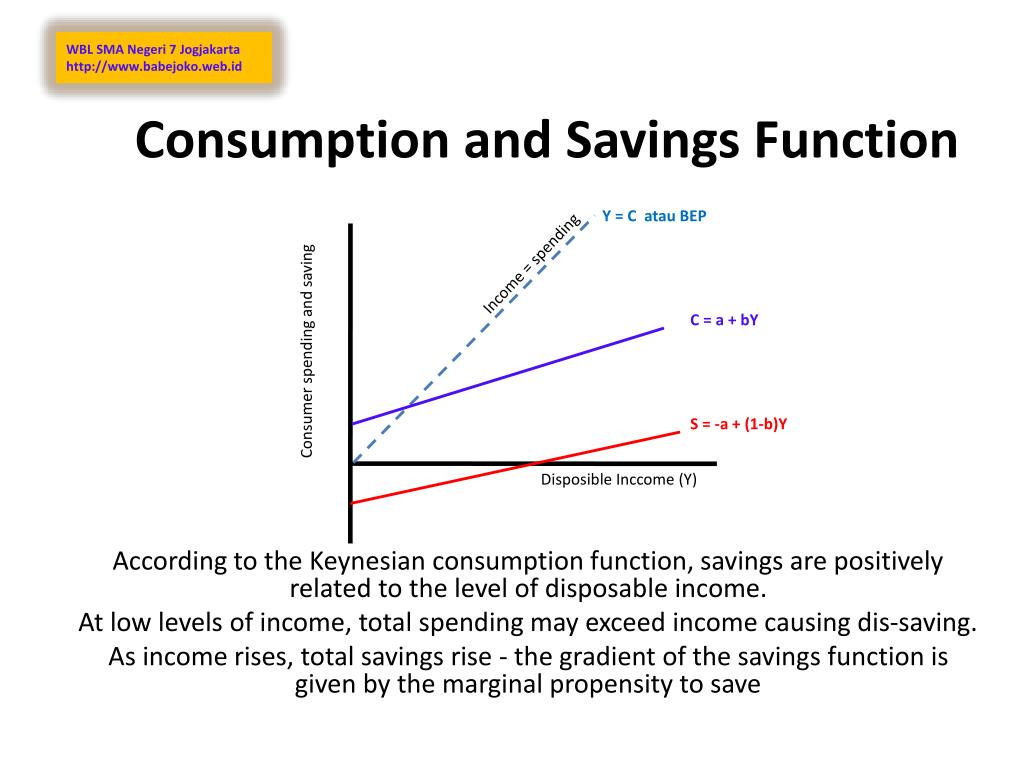
Ppt Consumption And Savings Function Powerpoint Presentation Free The consumption function is a mathematical formula that represents the functional relationship between total consumption and gross national income. aggregate savings should increase. Definition, equation derivation & graph. savings represent the portion of income that is not consumed on goods and services. it is obtained by deducting consumption expenditures from disposable income. individuals set aside a portion of their income as savings to meet their future needs related to investment, contingencies, and retirement.
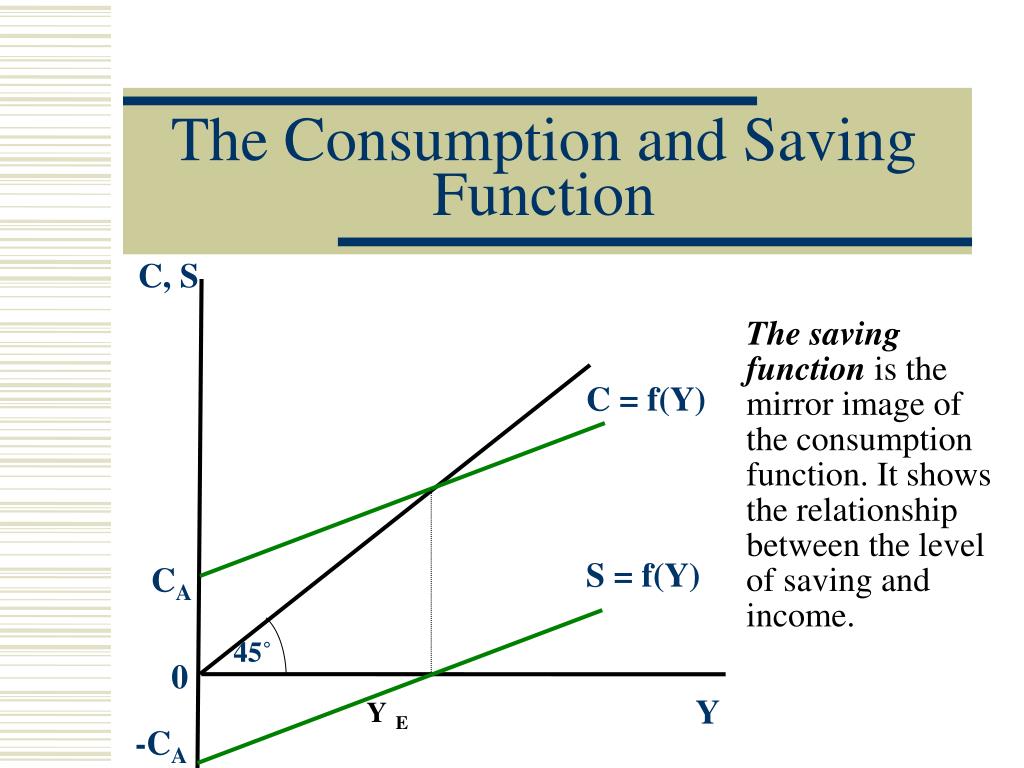
Ppt Consumption Saving S And Investment Powerpoint Presentation The consumption function is plotted in the upper part of the graph. at points along the 45 degree line, the values on the two axes are equal; we can measure personal saving as the distance between the 45 degree line and consumption. the curve of the saving function is in the lower portion of the graph. The consumption function is expressed as: advertisements: c = a by (a > 0, 0 < b < 1). where c and y represent real consumption and real income, respectively. the equation indicates that consumption is a linear function of income. in the equation, ‘a’ and ‘b’ are constants, called parameters. 16.21. consumption and saving. the consumption function is a relationship between current disposable income and current consumption. it is intended as a simple description of household behavior that captures the idea of consumption smoothing. we typically suppose the consumption function is upward sloping but has a slope less than one. Consumption is a function of the current absolute income of the consumer, not past or future income. the marginal propensity to consume (mpc) is less than 1, i.e., 1 > ∆c ∆y > 0. for instance, if the income is increased by 10 dollars, only part of it will be consumed and part of it will be saved. there is a positive correlation between.
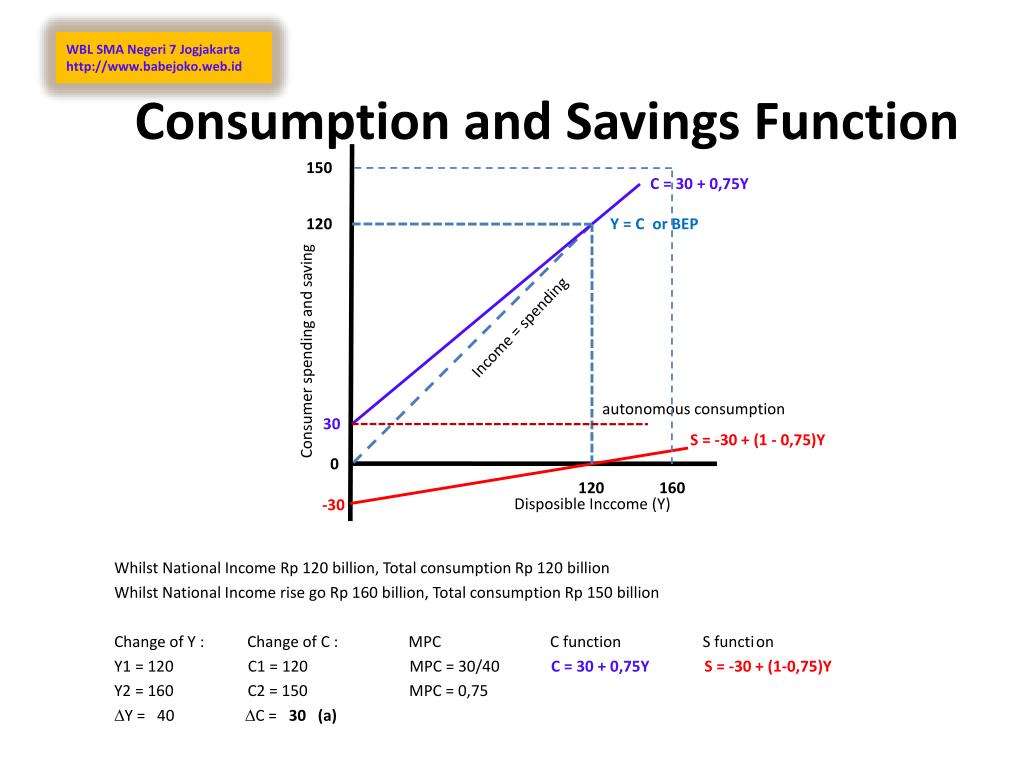
Ppt Consumption And Savings Function Powerpoint Presentation Free 16.21. consumption and saving. the consumption function is a relationship between current disposable income and current consumption. it is intended as a simple description of household behavior that captures the idea of consumption smoothing. we typically suppose the consumption function is upward sloping but has a slope less than one. Consumption is a function of the current absolute income of the consumer, not past or future income. the marginal propensity to consume (mpc) is less than 1, i.e., 1 > ∆c ∆y > 0. for instance, if the income is increased by 10 dollars, only part of it will be consumed and part of it will be saved. there is a positive correlation between. The consumption function is plotted in the upper part of the graph. at points along the 45 degree line, the values on the two axes are equal; we can measure personal saving as the distance between the 45 degree line and consumption. the curve of the saving function is in the lower portion of the graph. 0. where u is a strictly increasing and strictly concave utility function, cj. denotes consumption in period t, aj t 1 denotes saving in period t (equivalently, the assets in the beginning of period. 1), `j.

Consumption Function Saving Function Macroeconomics Class 12 By The consumption function is plotted in the upper part of the graph. at points along the 45 degree line, the values on the two axes are equal; we can measure personal saving as the distance between the 45 degree line and consumption. the curve of the saving function is in the lower portion of the graph. 0. where u is a strictly increasing and strictly concave utility function, cj. denotes consumption in period t, aj t 1 denotes saving in period t (equivalently, the assets in the beginning of period. 1), `j.

Comments are closed.