Complementary Angles Gcse Maths Steps Examples Worksheets Library

Complementary Angles Gcse Maths Steps Examples Worksheets Library The two angles are complementary and therefore equal 90°. 2 clearly identity which of the unknown angles the question is asking you to find the value of. find the angle that is not 17°. 3 solve the problem and give reasons where applicable. 4 clearly state the answer using angle terminology. Adding the angles together, we can form the expression. 70 90 = 160.70 90 = 160. 2 subtract the angle sum from 180 o180o. as the sum of angles on a straight line total 180 o, 180o, 180 − 160 = 20.180 −160 = 20. 3 form and solve the equation. here we have no equation to solve as the missing angle is 20 o.20o.
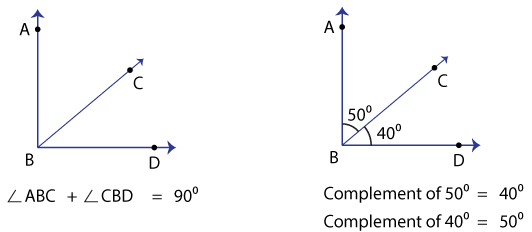
Complementary Angles Gcse Maths Steps Examples Worksheets Library Example 1: angles on a straight line. find angles a and b. identify which angle you need to find (label it if you need to). you need to find angles labelled a and b. 2 identify which angle rule s apply to the context and write them down (remember multiple rules may be needed). Download for free complimentary angles worksheet #359808, download othes for free. Note that you will lose points if you ask for hints or clues! 1) calculate the complementary angles for. a) 20˚. complementary angle = degrees. b) 45˚. complementary angle = degrees. c) 62˚. complementary angle = degrees. d) 87˚. The following diagrams show examples of complementary and supplementary angles. scroll down the page for more examples and step by step explanations. angles in a right angle add up to 90°. when the sum of two angles is 90° those two angles are complementary angles. when the sum of two angles is 180° those two angles are supplementary angles.
Angles Gcse Maths Steps Examples Worksheet Worksheets L Note that you will lose points if you ask for hints or clues! 1) calculate the complementary angles for. a) 20˚. complementary angle = degrees. b) 45˚. complementary angle = degrees. c) 62˚. complementary angle = degrees. d) 87˚. The following diagrams show examples of complementary and supplementary angles. scroll down the page for more examples and step by step explanations. angles in a right angle add up to 90°. when the sum of two angles is 90° those two angles are complementary angles. when the sum of two angles is 180° those two angles are supplementary angles. Complementary angles vs supplementary angles. complementary angles and supplementary angles both involve pairs of angles that have specific relationships with each other. complementary angles. complementary angles are two angles that when added together, result in `90°`. they can either be adjacent or non adjacent. 40 degrees x = 90 degrees (the sum of the two complementary angles) x = 90 – 40 = 50 degrees. therefore, the measure of the other acute angle in the triangle is 50 degrees. example 3: the measure of one angle of a triangle is 30 degrees less than its complementary angle. find the measures of the two angles. solution:.

Complementary Angles Gcse Maths Steps Examples Worksheets Library Complementary angles vs supplementary angles. complementary angles and supplementary angles both involve pairs of angles that have specific relationships with each other. complementary angles. complementary angles are two angles that when added together, result in `90°`. they can either be adjacent or non adjacent. 40 degrees x = 90 degrees (the sum of the two complementary angles) x = 90 – 40 = 50 degrees. therefore, the measure of the other acute angle in the triangle is 50 degrees. example 3: the measure of one angle of a triangle is 30 degrees less than its complementary angle. find the measures of the two angles. solution:.

Comments are closed.