Circular Motion Acceleration Angular Tangential Centripetal
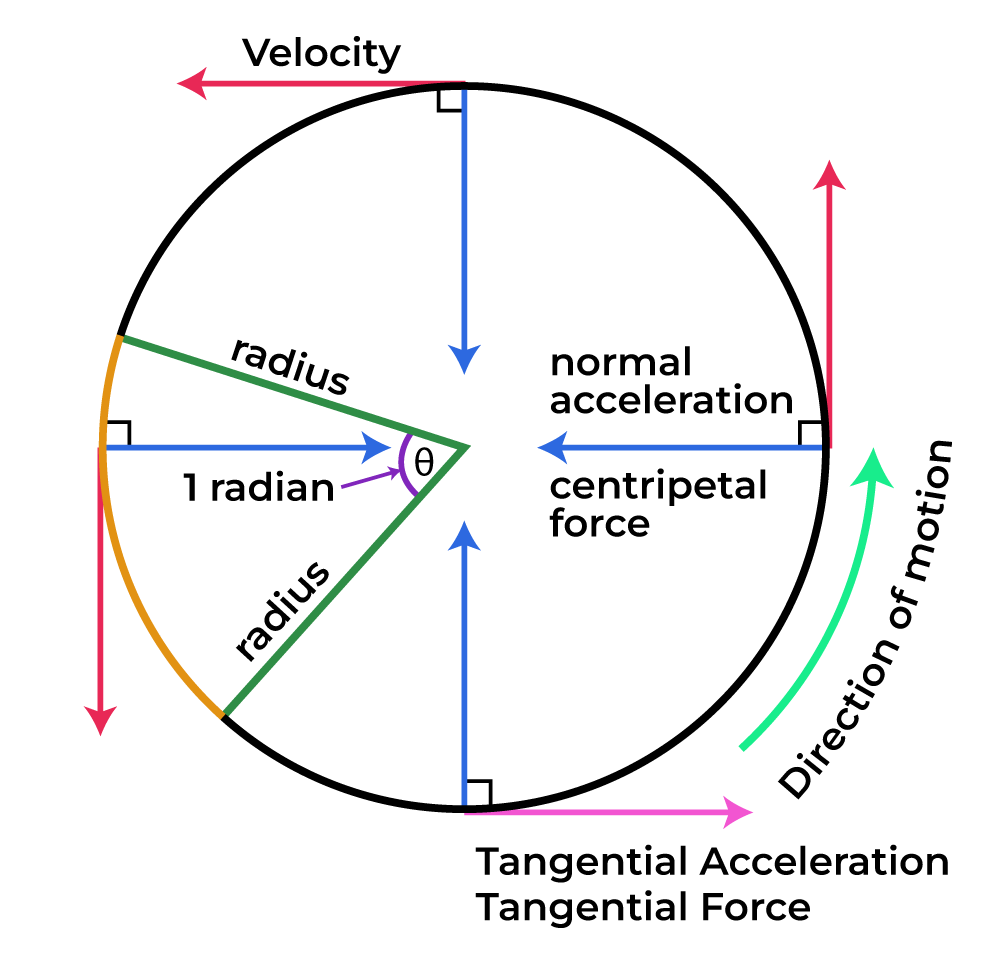
Tangential Acceleration Definition Formula Solved Examples The direction of tangential acceleration is tangent to the circle whereas the direction of centripetal acceleration is radially inward toward the center of the circle. thus, a particle in circular motion with a tangential acceleration has a total acceleration that is the vector sum of the centripetal and tangential accelerations:. We call the acceleration of an object moving in uniform circular motion the centripetal acceleration a c because centripetal means center seeking. figure 6.7 the directions of the velocity of an object at two different points are shown, and the change in velocity Δ v Δ v is seen to point approximately toward the center of curvature (see small.
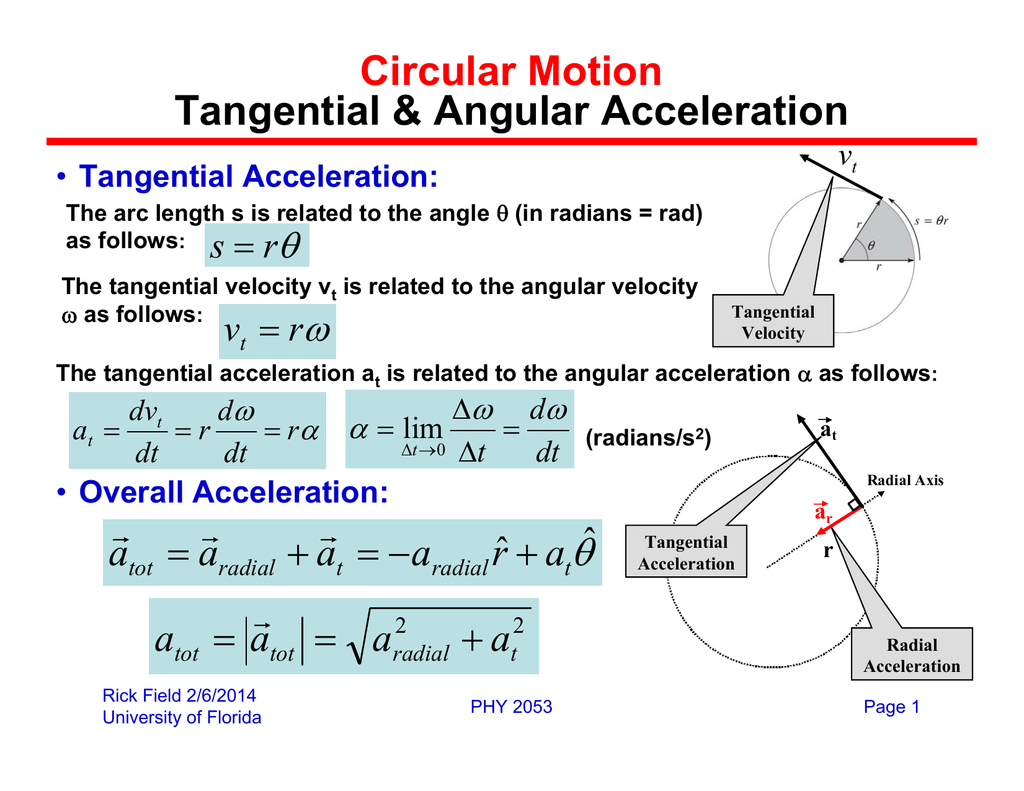
Circular Motion Tangential Angular Acceleration оё Answer: t = 8 seconds. 2(64 rev ) = 8 s. (2 rev s. 2 ) an astronaut is being tested in a centrifuge. the centrifuge has a radius r and, in starting from rest at t = 0, rotates with a constant angular acceleration α = 0.25 rad s2 . at what time t > 0 is the magnitude of the tangential acceleration equal to the magnitude of the radial. Unlike tangential acceleration, centripetal acceleration is present in both uniform and non uniform circular motion. in a non uniform circular motion, normal force does not always point in the opposite direction of weight. here is an example with an object traveling in a straight path then looping a loop back into a straight path again. The direction of tangential acceleration is tangent to the circle whereas the direction of centripetal acceleration is radially inward toward the center of the circle. thus, a particle in circular motion with a tangential acceleration has a total acceleration that is the vector sum of the centripetal and tangential accelerations:. If the speed of the particle is changing, the centripetal acceleration at any instant is (still) given by equation 18a.5 18a.5 with the v v being the speed of the particle at that instant (and in addition to the centripetal acceleration, the particle also has some along the circular path acceleration known as tangential acceleration).
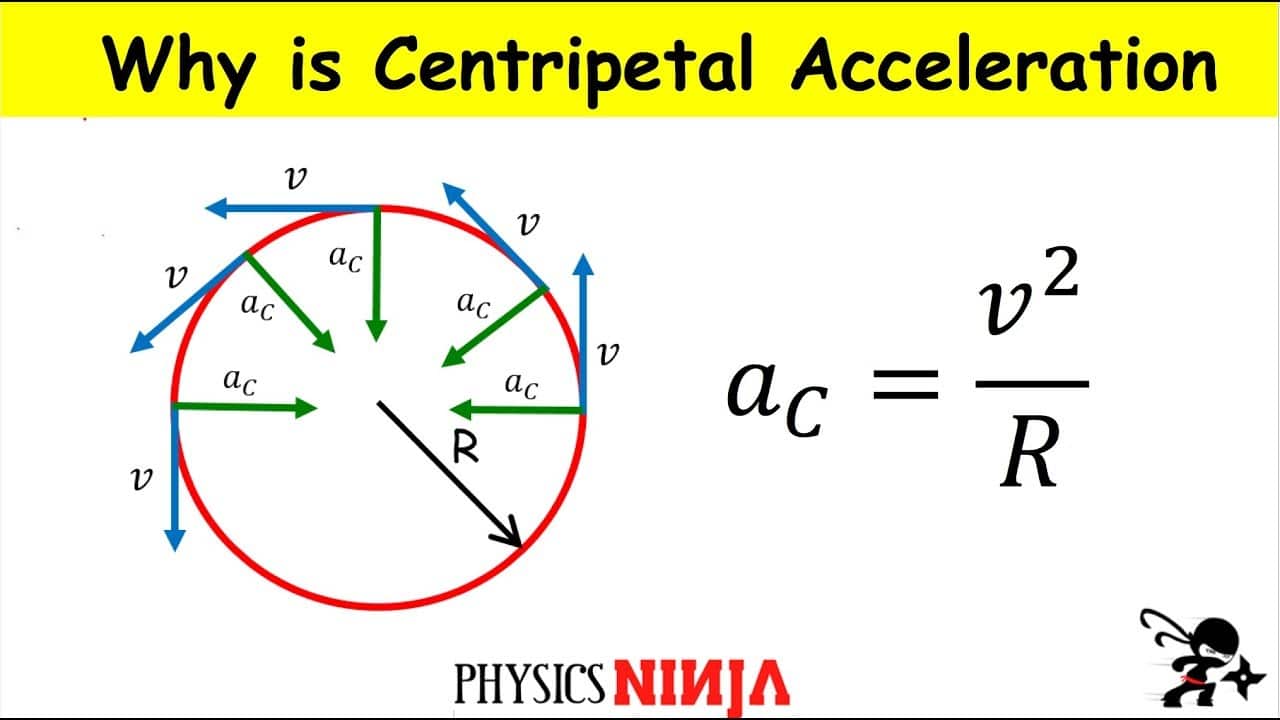
What Are Centripetal Acceleration Formula Easy Example Get Education Bee The direction of tangential acceleration is tangent to the circle whereas the direction of centripetal acceleration is radially inward toward the center of the circle. thus, a particle in circular motion with a tangential acceleration has a total acceleration that is the vector sum of the centripetal and tangential accelerations:. If the speed of the particle is changing, the centripetal acceleration at any instant is (still) given by equation 18a.5 18a.5 with the v v being the speed of the particle at that instant (and in addition to the centripetal acceleration, the particle also has some along the circular path acceleration known as tangential acceleration). Centripetal acceleration. if our object is increasing its speed or slowing down, there is also a non zero tangential acceleration in the direction of motion. but when the object is moving at a constant speed in a circle then only the centripetal acceleration is non zero. 1 . joni mitchell, the circle game, siquomb publishing company. 1. Summary. uniform circular motion is motion in a circle at constant speed. centripetal acceleration →a c a → c is the acceleration a particle must have to follow a circular path. centripetal acceleration always points toward the center of rotation and has magnitude ac = v2 r. a c = v 2 r.

Comments are closed.