Chemistry The Chemical And Physical Properties Of Bread
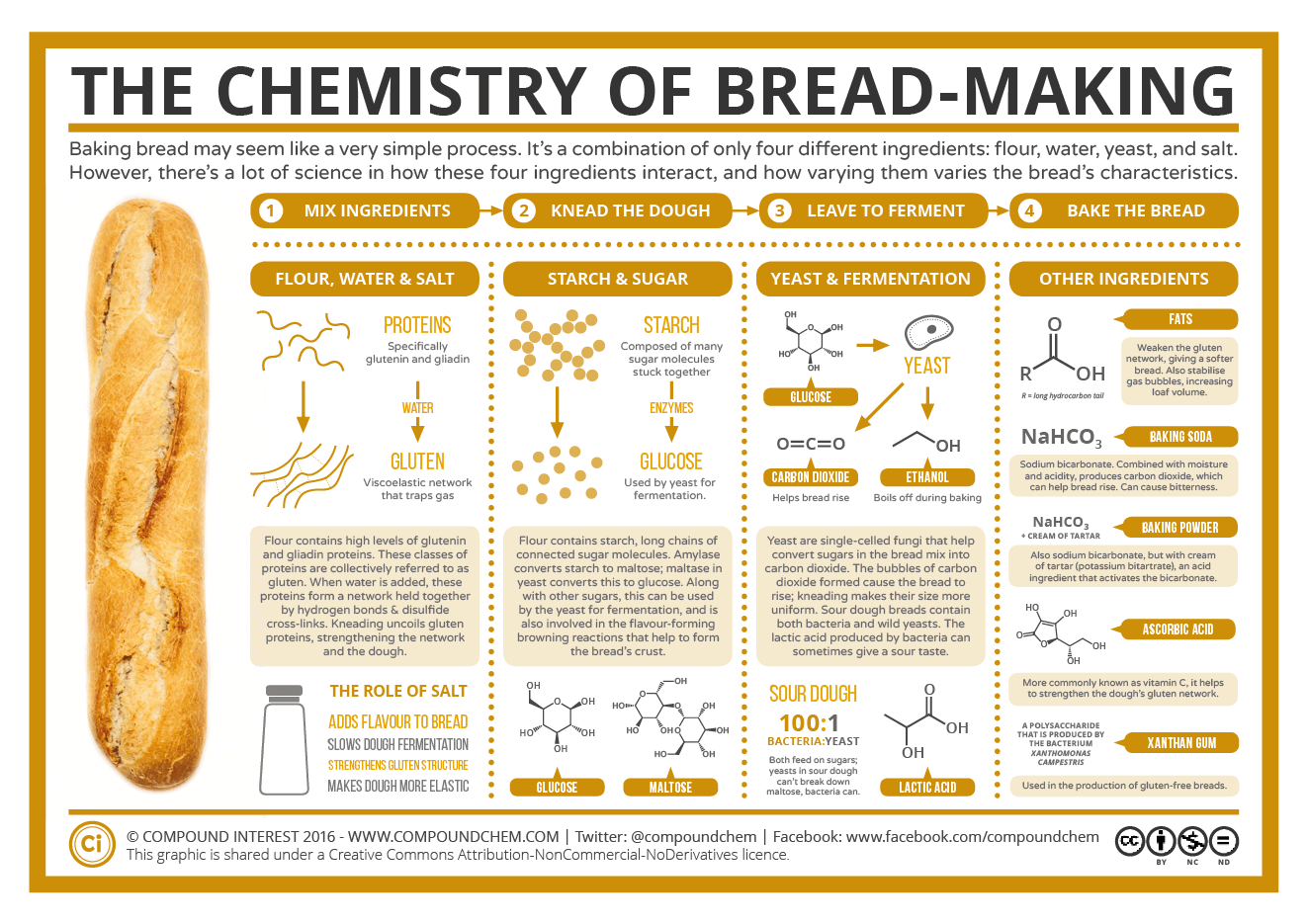
Baking Bread The Chemistry Of Bread Making Compound Interest The process of making bread can be broken down at a very simple level into four steps. first, the ingredients are mixed; the four basic ingredients used to make bread are flour, water, yeast, and salt. combining these creates a dough, which is then kneaded before being left to rise, before being baked. In short. a series of chemical reactions take place throughout the process of turning flour into bread. bread owes much of its structure to gluten proteins – a key target for chemists looking to intervene in the process. traditional bread making is a slow process, prompting scientists to develop ‘no time’ doughs.
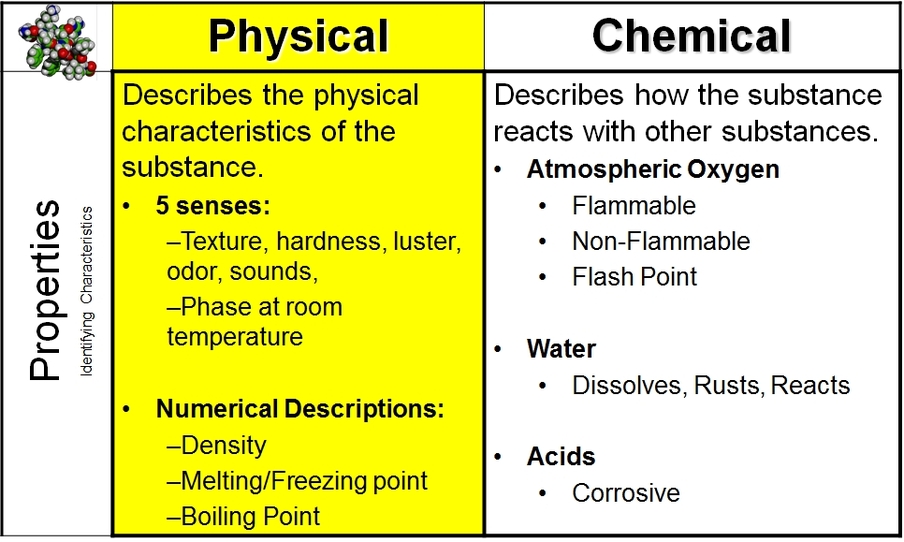
Chemical Physical Properties Vista Heights 8th Grade Science Bread. also stabilise gas bubbles, increasing loaf volume. o r oh r = long hydrocarbon tail xanthan gum used in the production of gluten free breads. 1 mix ingredients 2 knead the dough 3 leave to ferment 4 bake the bread a polysaccharide that is produced by the bacterium xanthomonas campestris. Purpose: by baking a loaf of bread, students will learn how chemical changes can alter physical properties. after analyzing the chemical reactions that occur in breadmaking and observing how they. The key role of the yeast in bread making is acting. as leavening agents. the enzymes in the our and yeast breakdo wn starch to sugars. which are then fermented by the yeast, primarily to co 2 and. The quality assessment of bread makes use of determinations of its physical properties, among which the most frequently tested are the volume, weight, and specific weight (true density) of bread. estimations of the quality of bread crumb take into consideration such features as its structure, moisture, and mechanical properties (firmness.

Comments are closed.