Centripetal Acceleration And Tangential Velocity For A Spinning Disk

Centripetal Acceleration And Tangential Velocity For A Spinning Disk The spin rate of a disk is given in rpm. we calculate the period and get centripetal acceleration from a=4pi^2r t^2. then we calculate angular velocity to. Answer: t = 8 seconds. 2(64 rev ) = 8 s. (2 rev s. 2 ) an astronaut is being tested in a centrifuge. the centrifuge has a radius r and, in starting from rest at t = 0, rotates with a constant angular acceleration α = 0.25 rad s2 . at what time t > 0 is the magnitude of the tangential acceleration equal to the magnitude of the radial.
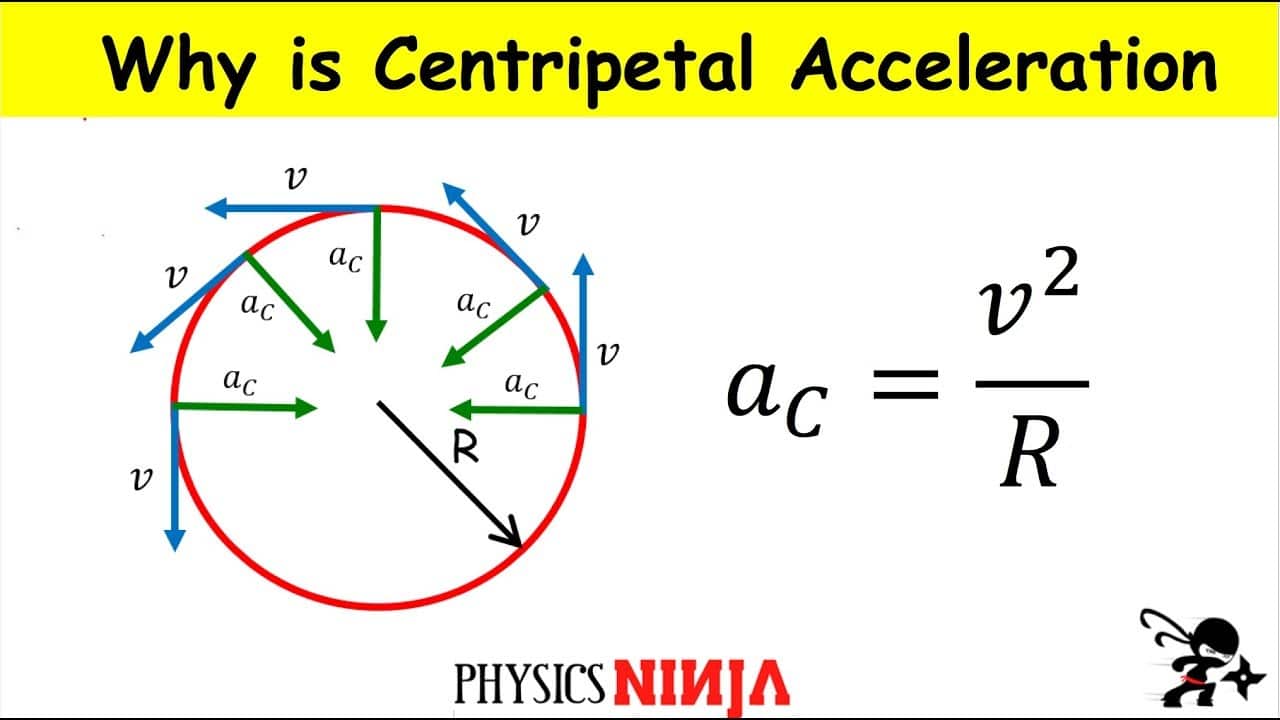
What Are Centripetal Acceleration Formula Easy Example Get Education Bee Calculate the centripetal acceleration of a point 7.50 cm from the axis of an ultracentrifuge spinning at 7.5 × 10 4 rev min. 7.5 × 10 4 rev min. determine the ratio of this acceleration to that due to gravity. Substituting v = rω v = r ω into the above expression, we find ac = (rω2) r = rω2 a c = (r ω 2) r = r ω 2. we can express the magnitude of centripetal acceleration using either of two equations: ac = v2 r; ac = rω2 (6.2.5) (6.2.5) a c = v 2 r; a c = r ω 2. recall that the direction of ac a c is toward the center. Figure 10.4(a)), a centripetal acceleration toward the center, and a component tangent to the circular path, which is called the tangential acceleration . if the turntable slows down, then the tangential acceleration reverses direction (see figure 10.4(b)), as does the angular acceleration (because the angular. The point was rotating at 25 rev min, and has increased to 45 rev min over the last 18 seconds. this is rotational acceleration. centripetal acceleration (also known as radial acceleration) if the "point" on the disk has mass then there has to be some kind of force that points to the center of the disk "keeping" the point in its circular motion.
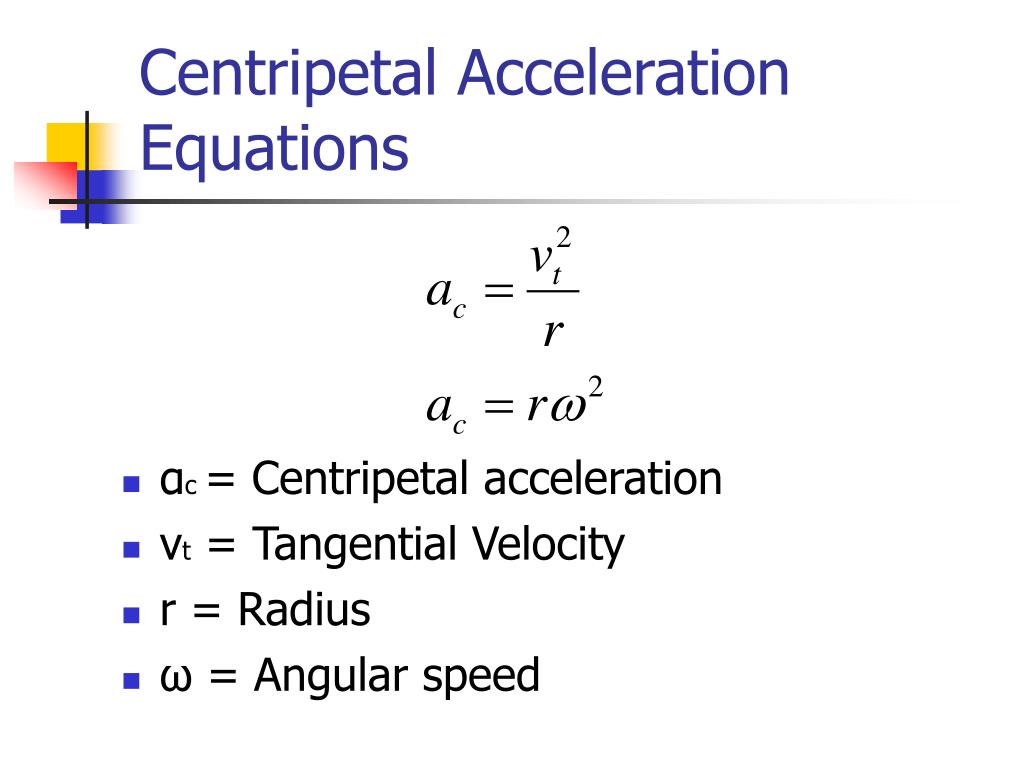
Ppt Tangential And Centripetal Acceleration Powerpoint Presentation Figure 10.4(a)), a centripetal acceleration toward the center, and a component tangent to the circular path, which is called the tangential acceleration . if the turntable slows down, then the tangential acceleration reverses direction (see figure 10.4(b)), as does the angular acceleration (because the angular. The point was rotating at 25 rev min, and has increased to 45 rev min over the last 18 seconds. this is rotational acceleration. centripetal acceleration (also known as radial acceleration) if the "point" on the disk has mass then there has to be some kind of force that points to the center of the disk "keeping" the point in its circular motion. We call the acceleration of an object moving in uniform circular motion the centripetal acceleration a c because centripetal means center seeking. figure 6.7 the directions of the velocity of an object at two different points are shown, and the change in velocity Δ v Δ v is seen to point approximately toward the center of curvature (see small. Centripetal acceleration ac a c is the acceleration experienced while in uniform circular motion. it always points toward the center of rotation. it is perpendicular to the linear velocity v v and has the magnitude. ac = a c = v2 r v 2 r ; ac = rω2.; a c = r ω 2. the unit of centripetal acceleration is m s2. m s 2.

Comments are closed.