Catalysis A Catalyst Is A Substance That Increases The Rate Of A

What Is A Catalyst Understand Catalysis Catalysis. an air filter that uses a low temperature oxidation catalyst to convert carbon monoxide to less toxic carbon dioxide at room temperature. it can also remove formaldehyde from the air. catalysis ( kəˈtæləsɪs ) is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst[1][2] ( ˈkætəlɪst ). In chemistry and biology, a catalyst is a substance the increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by it. catalysis is the process of speeding up a reaction using a catalyst. the word “catalyst” comes from the greek word kataluein, which means to loosen or untie. british chemistry elizabeth fulhame first described the.

Catalysts Enzymes вђ Overview Examples Expii A catalyst is a chemical substance that affects the rate of a chemical reaction by altering the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed. this process is called catalysis. a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction and it may participate in multiple reactions at a time. the only difference between a catalyzed reaction and an. Thus a catalyst (in this case, sulfuric acid) can be used to speed up a reversible reaction such as ester formation or its reverse, ester hydrolysis: figure 17.6.1 17.6. 1: an acid catalyzed reactions. the catalyst has no effect on the equilibrium constant or the direction of the reaction. The reactant in an enzyme catalyzed reaction is called a substrate. enzyme inhibitors cause a decrease in the reaction rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction. 14.7: catalysis. catalysts participate in a chemical reaction and increase its rate. they do not appear in the reaction’s net equation and are not consumed during the reaction. Catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. enzymes are naturally occurring catalysts responsible for many essential biochemical reactions. in general, catalytic action is a chemical reaction between the catalyst and a reactant.

Catalysis A Catalyst Is A Substance That Increases The Rate Of A The reactant in an enzyme catalyzed reaction is called a substrate. enzyme inhibitors cause a decrease in the reaction rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction. 14.7: catalysis. catalysts participate in a chemical reaction and increase its rate. they do not appear in the reaction’s net equation and are not consumed during the reaction. Catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. enzymes are naturally occurring catalysts responsible for many essential biochemical reactions. in general, catalytic action is a chemical reaction between the catalyst and a reactant. Exercise 12.8.1 12.8. 1. determine which of the two diagrams here (both for the same reaction) involves a catalyst, and identify the activation energy for the catalyzed reaction: in this figure, two graphs are shown. the x axes are labeled, “extent of reaction,” and the y axes are labeledc “energy (k j).”. Catalysis, the modification of the rate of a chemical reaction, usually an acceleration, by addition of a substance not consumed during the reaction. each catalyst molecule may induce the transformation of many molecules of reactants. learn about the history, classification, and reactions of catalysis.
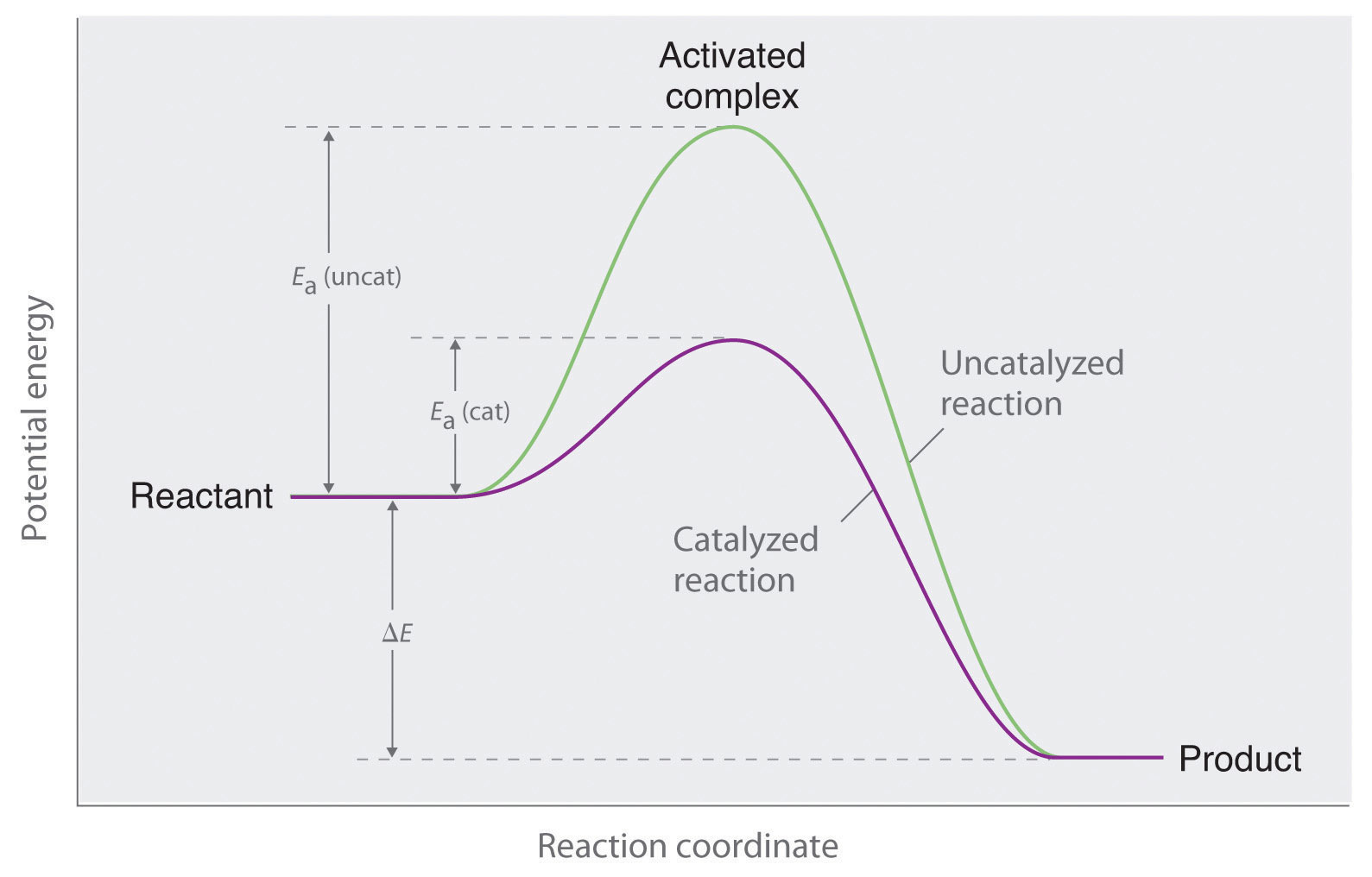
Catalysis Exercise 12.8.1 12.8. 1. determine which of the two diagrams here (both for the same reaction) involves a catalyst, and identify the activation energy for the catalyzed reaction: in this figure, two graphs are shown. the x axes are labeled, “extent of reaction,” and the y axes are labeledc “energy (k j).”. Catalysis, the modification of the rate of a chemical reaction, usually an acceleration, by addition of a substance not consumed during the reaction. each catalyst molecule may induce the transformation of many molecules of reactants. learn about the history, classification, and reactions of catalysis.

Catalysis A Catalyst Is A Substance That Increases The Rate Of A

Comments are closed.