Biochemical Differences In Human Breast Milk Contents According To
Biochemical Differences In Human Breast Milk Contents According To Biochemical differences in human breast milk contents according to infant’s gender. j mol biol biotech. vol.3 no.1:2 introduction breast milk is the main source of energy and nutrients for the growing infant [1]. it provides all the needed requirements and protects against infections and diseases in both the infant and the mother [2]. Human breast milk (hbm) is essential for the infant’s growth and development right after birth and is an irreplaceable source of nutrition for early human survival [1,2]. for this reason, the world health organization and united nations children’s fund recommend exclusive hbm feeding for at least 6 months after birth and to continue for up.

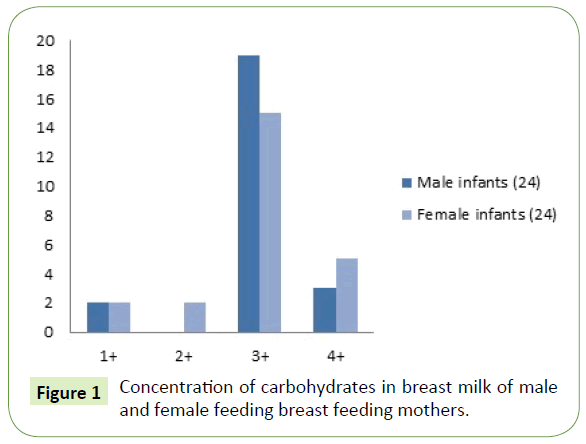
Pdf Biochemical Differences In Human Breast Milk Contents Accordin Pdf | on aug 6, 2018, salma dafaallah and others published biochemical differences in human breast milk contents according to infant’s gender | find, read and cite all the research you need on. How to cite this article: salma dafaallah, mutaz amin, amar mohammed, eman kabbara, biochemical differences in human breast milk contents according to infant’s gender. anatomy physiol biochem int j: 2018; 5(3): 555661. doi: 10.19080 apbij.2018.05.555661. breast feeding infants respectively. the result was statistically significant (p value. The fat content in hbm is affected by differences in dietary habits, maternal diet, weight change during pregnancy, and breast fullness including last feeding time. immediately after birth, colostrum, the first hbm produced after birth, contains 15–20 g l fat, but it gradually increases with lactation, reaching 40 g l in mature milk. Breast milk contains many complex proteins, lipids and carbohydrates, the concentrations of which alter dramatically over a single feed, as well as over lactation, to reflect the infant's needs. in addition to providing a source of nutrition for infants, breast milk contains a myriad of biologically active components.

Comments are closed.