Are You Ready To Learn About The Ventilator Modes Of Mechanical

Ventilator Modes Made Easy Study Guide For Mechanical Ventilation In Ventilator modes made easy! are you ready to learn all of the modes of mechanical ventilation?💥 full guide on ventilator modes bit.ly 2rtlgjow. Continuous mandatory ventilation (cmv) is a mode in which the ventilator takes full control of the patient’s breathing by delivering a preset tidal volume at a specific, time triggered frequency. this mode is predominantly used for patients who are fully sedated and have received neuromuscular blocking agents.

Are You Ready To Learn About The Ventilator Modes Of Mechanical Mechanical ventilation is a medical procedure that assists or replaces spontaneous breathing by using a machine called a ventilator. it delivers air to the lungs, usually through a tube inserted into the trachea, ensuring adequate oxygenation and carbon dioxide removal for patients unable to breathe independently. The key ventilator settings are tidal volume, fio2, peep, and the ventilation mode. tidal volume ensures adequate ventilation, fio2 is vital for oxygenation, peep keeps alveoli open, and the ventilation mode coordinates the machine’s support with patient efforts. these parameters are crucial for effective and safe respiratory support. Basic modes of mechanical ventilation: niall d. ferguson, md, frcpc, msc head of critical care medicine university health network & sinai health system professor, departments of medicine & physiology, institute of health policy, management and evaluation interdepartmental division of critical care medicine university of toronto. Mechanical ventilation patients that are sedated, paralyzed or need to rest will need to be in this mode for proper ventilation. this mode allows the patient’s breathing to be “controlled”. if the patient begins to actively participate in breathing this mode will become less effective and could lead to the patient over breathing.
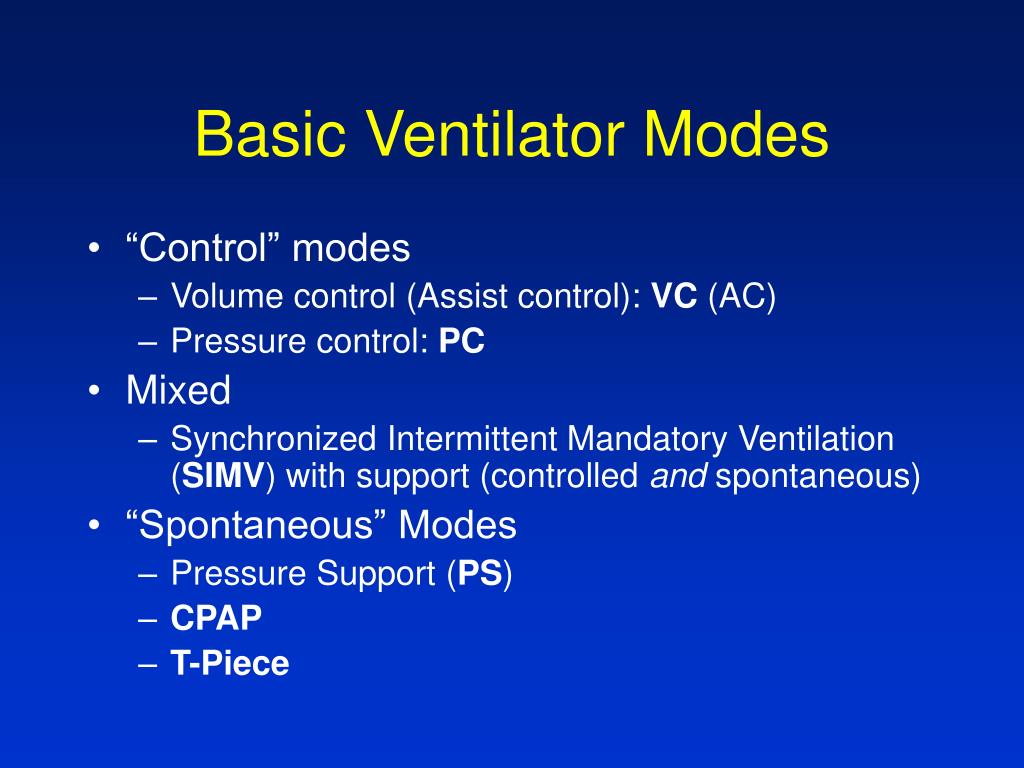
Ventilator Modes Mechanical Ventilation Lecture 7 Basic modes of mechanical ventilation: niall d. ferguson, md, frcpc, msc head of critical care medicine university health network & sinai health system professor, departments of medicine & physiology, institute of health policy, management and evaluation interdepartmental division of critical care medicine university of toronto. Mechanical ventilation patients that are sedated, paralyzed or need to rest will need to be in this mode for proper ventilation. this mode allows the patient’s breathing to be “controlled”. if the patient begins to actively participate in breathing this mode will become less effective and could lead to the patient over breathing. Mechanical ventilation. mechanical ventilation is a type of therapy that helps you breathe or breathes for you when you can’t breathe on your own. you might be on a ventilator during surgery or if your lungs aren’t working properly. mechanical ventilation keeps your airways open, delivers oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation explained with illustrations by dr. roger seheult. get cme ce for this video series here: medcram courses mechanica.
Ventilator Modes Made Easy Study Guide For Mechanical Ventilation Mechanical ventilation. mechanical ventilation is a type of therapy that helps you breathe or breathes for you when you can’t breathe on your own. you might be on a ventilator during surgery or if your lungs aren’t working properly. mechanical ventilation keeps your airways open, delivers oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation explained with illustrations by dr. roger seheult. get cme ce for this video series here: medcram courses mechanica.

Comments are closed.