Anatomy Of The Testis By Dr Meetu Agarwal
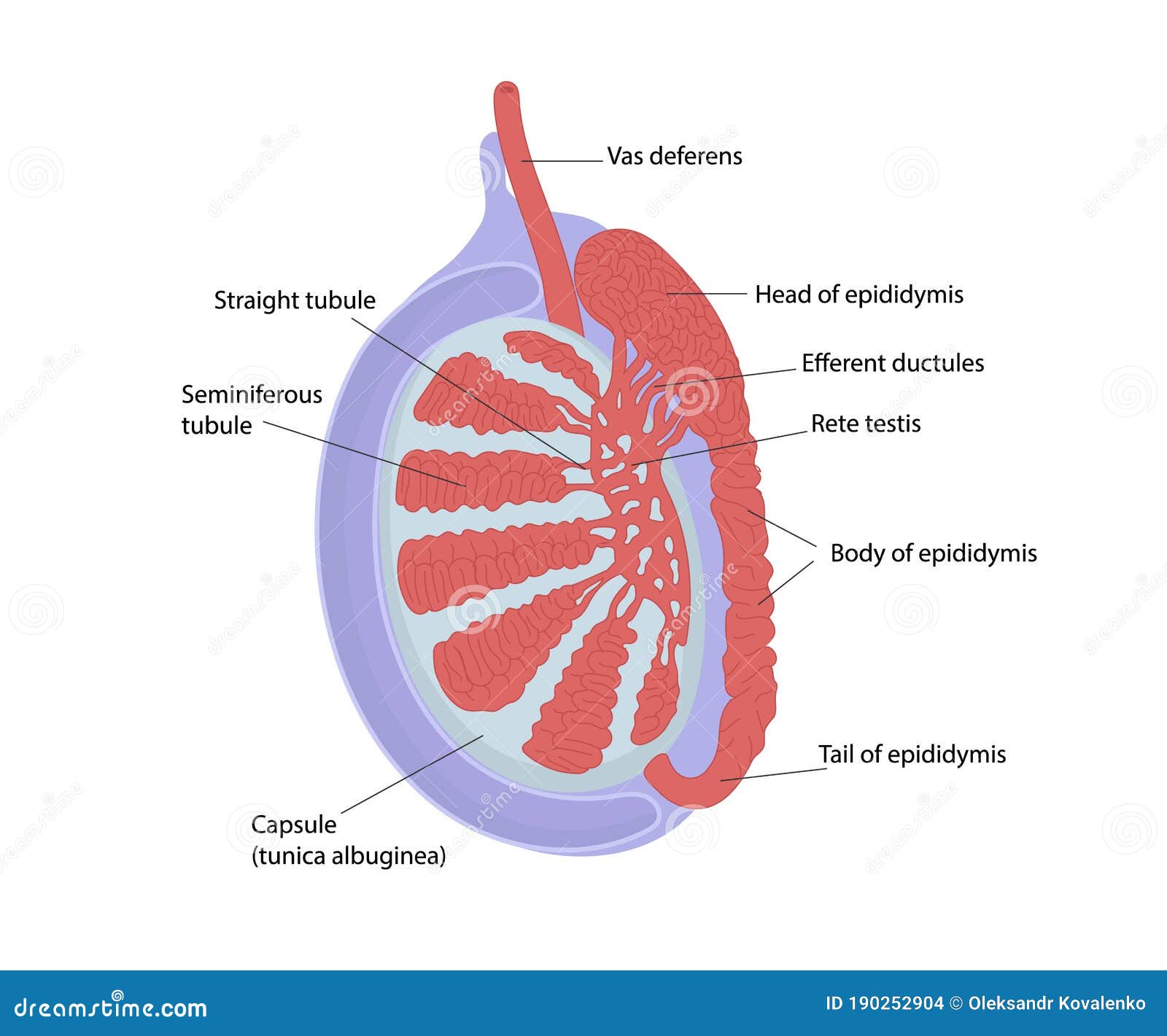
Labelled Diagram Of Testis Anatomy of the testis by dr. meetu agarwal. Gross anatomy of the testis. the testes are paired organs in the scrotum, 4 × 3 × 2.5 cm, 20–25 ml volume. the testicles have a strong organ capsule (tunica albuginea testis). the testicular parenchyma is composed of 250–350 lobules, which drain through the mediastinum testis to the epididymis. the lobules are separated by connective.
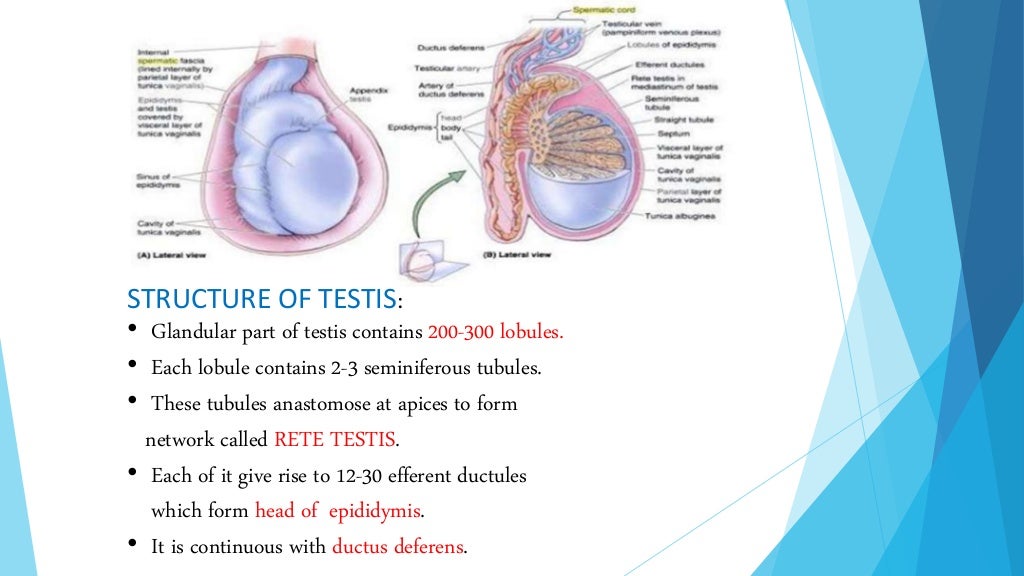
Anatomy Of Testis The testes (testicles) are male reproductive glands found in a saccular extension of the anterior abdominal wall called the scrotum. they are in ovoid shape, sized four to six centimeters in length. testes develop retroperitoneally on the posterior abdominal wall and descend to scrotum before birth. the scrotum is often asymmetric, with one. The male reproductive system includes the scrotum, which contains three major paired structures: 1. the testes. epididymis. spermatic cord. the layers of the scrotum are continuations of the abdominal wall layers, and from superficial to deep, the layers are: 2. s kin. d artos fascia and muscle. e xternal spermatic fascia. The testis is the male gonad that produces and stores sperm. it is oval shaped and suspended in the scrotum by the spermatic cord. the testis has three layers of coverings and is made up of lobules containing seminiferous tubules that produce sperm. sperm exit the testis via the rete testis and efferent ductules into the epididymis for storage. Dissection of anterior abdominal wall by dr.meetu agarwal.

Organization Of The Testis A A Cross Section Through A Testis The testis is the male gonad that produces and stores sperm. it is oval shaped and suspended in the scrotum by the spermatic cord. the testis has three layers of coverings and is made up of lobules containing seminiferous tubules that produce sperm. sperm exit the testis via the rete testis and efferent ductules into the epididymis for storage. Dissection of anterior abdominal wall by dr.meetu agarwal. The testes (singular: testis), commonly known as the testicles, are a pair of ovoid glandular organs that are central to the function of the male reproductive system. the testes are responsible for the production of sperm cells and the male sex hormone testosterone. the testes produce as many as 12 trillion sperm in a male's lifetime, about 400. The testes and epididymis are paired structures, located within the scrotum. the testes are the site of sperm production and hormone synthesis, while the epididymis has a role in the storage of sperm. in this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the testes and epididymis – their structure, vasculature, innervation and clinical correlations.

Anatomy Of Testis The testes (singular: testis), commonly known as the testicles, are a pair of ovoid glandular organs that are central to the function of the male reproductive system. the testes are responsible for the production of sperm cells and the male sex hormone testosterone. the testes produce as many as 12 trillion sperm in a male's lifetime, about 400. The testes and epididymis are paired structures, located within the scrotum. the testes are the site of sperm production and hormone synthesis, while the epididymis has a role in the storage of sperm. in this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the testes and epididymis – their structure, vasculature, innervation and clinical correlations.
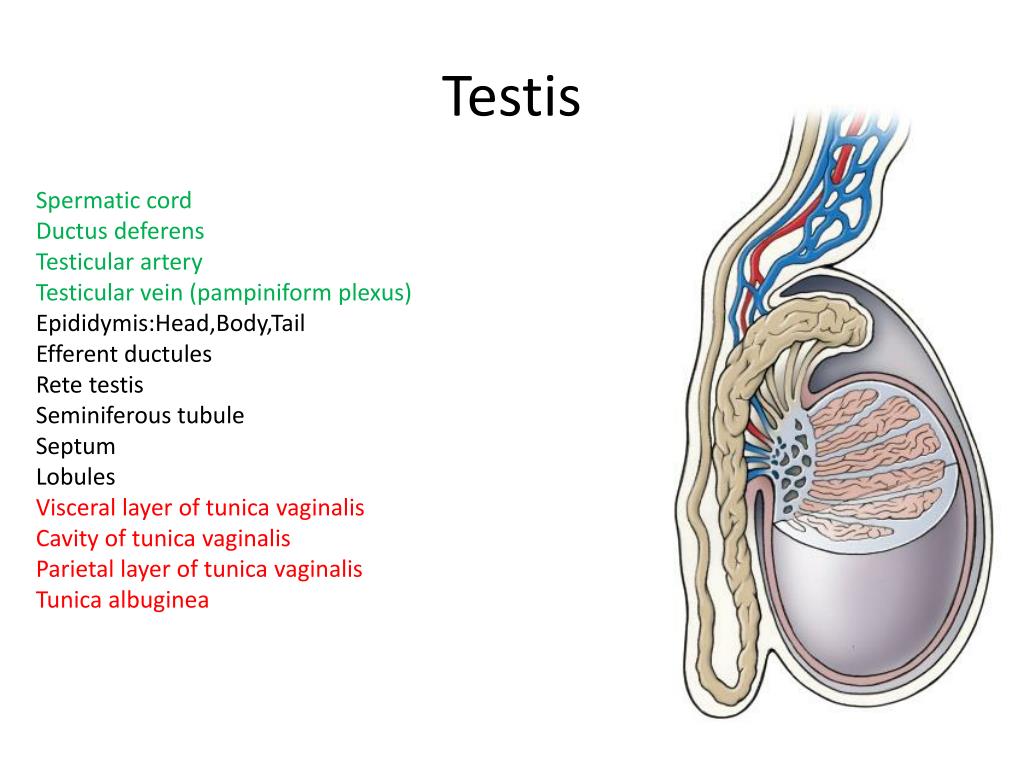
Labelled Diagram Of Testis

Comments are closed.