Anatomy Of The Canine Hyoid Apparatus
The Respiratory System Veterian Key It is attached to the temporal region of the skull by a synchondrosis joint. it is palpable through the pharynx and is visible when the pharynx is viewed through the mouth. the basihyoid is palpable within the intermandibular space. the sternohyoid muscle pulls the hyoid caudally and the geniohyoid muscle pulls the hyoid rostrally. Following overwhelming demand from our dedicated veterinary student community, we're thrilled to launch a brand new series of captivating animations that bri.

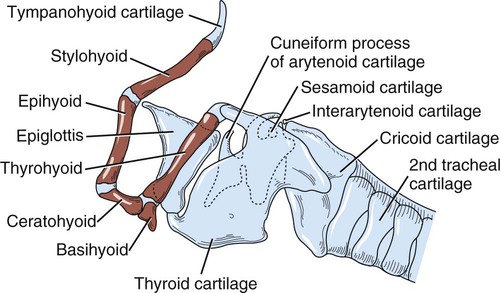
Fig 2 34 Hyoid Apparatus And Larynx Suspended From Temporal Region Of The dog throat anatomy starts from the epiglottis and extends to the esophagus and trachea. there is no specific boundary of the throat area in the dogs. you will find the hyoid apparatus in front of the dog’s throat. collectively, you may find the below mentioned organs or structures in a dog’s throat –. Canine anatomy. the larynx is attached to the first ring of the trachea and is suspended ventral to the esophagus by the hyoid apparatus (figures 101 1 and 101 2). structurally, it is formed by epiglottic, thyroid, cricoid, sesamoid, interarytenoid, and paired arytenoid cartilages. 28 the epiglottis is the rostral most cartilage. Typically the pharynx has the widest lumen, followed by the larynx and then trachea, which is mildly smaller in diameter. a ratio between tracheal diameter and thoracic inlet height is proportionally larger in dogs with greater body weight and smaller in brachycephalic breeds. 4. fig. 26 1 normal lateral canine pharyngeal laryngeal region. The hyoid apparatus is a hollow, box like structure consisting of a number of cartilages connected by muscle and connective tissue. the most rostral of these cartilages, the epiglottis , is composed of elastic cartilage and is responsible for sealing off the entrance to the larynx or glottis when an animal swallows.

Dog Hyoid Apparatus Diagram Quizlet Typically the pharynx has the widest lumen, followed by the larynx and then trachea, which is mildly smaller in diameter. a ratio between tracheal diameter and thoracic inlet height is proportionally larger in dogs with greater body weight and smaller in brachycephalic breeds. 4. fig. 26 1 normal lateral canine pharyngeal laryngeal region. The hyoid apparatus is a hollow, box like structure consisting of a number of cartilages connected by muscle and connective tissue. the most rostral of these cartilages, the epiglottis , is composed of elastic cartilage and is responsible for sealing off the entrance to the larynx or glottis when an animal swallows. The hyoid apparatus (figures 7.1 and 7.7) is composed of several small bones, the phylogenetic remnants of some of the gill arches in fishes. it sits in the throat at the base of the tongue and supports the tongue and laryngeal muscles. it is composed of a median bar, the basihyoid or body, which is oriented transversely at the anterior end of. The larynx is suspended from the hyoid apparatus. it is bilaterally symmetrical and 'tube shaped' and can be described as a musculocartilagenous organ. the larynx moves position when the animal swallows due to its attachments to the tongue and the basihyoid bone of the hyoid apparatus by the thyrohyoid membrane. synovial joints.
Vm 525 Hyoid Apparatus Video Presentation Msu Mediaspace The hyoid apparatus (figures 7.1 and 7.7) is composed of several small bones, the phylogenetic remnants of some of the gill arches in fishes. it sits in the throat at the base of the tongue and supports the tongue and laryngeal muscles. it is composed of a median bar, the basihyoid or body, which is oriented transversely at the anterior end of. The larynx is suspended from the hyoid apparatus. it is bilaterally symmetrical and 'tube shaped' and can be described as a musculocartilagenous organ. the larynx moves position when the animal swallows due to its attachments to the tongue and the basihyoid bone of the hyoid apparatus by the thyrohyoid membrane. synovial joints.

Comments are closed.