Anatomy Of The Bladder Wall Trial Exhibits Inc

Anatomy Of The Bladder Wall Trial Exhibits Inc Add to collection. exhibit id: ur c 0232. anatomy of the bladder wall. this medical illustration shows the sagittal and cross sectional views of the bladder wall. the bladder wall encompasses the peritoneal space, perivesical fat, muscularis propria, lamina propria, urothelium, and bladder lumen. add to collectioncontact us. Anterior view of the anatomy of the bladder with a camera inserted.

Bladder Wall Anatomy Download Scientific Diagram The anterior view of the anatomy of the urinary system with an enlarged view of the bladder. the urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The gross anatomy of the bladder is divided into three major parts: the apex, the body, and the base. the bladder wall is a soft tissue that exhibits load history the first clinical trial. The urinary bladder functions as a storage vessel for urine to delay the frequency of urination. it is one of the most elastic organs of the body and is able to increase its volume greatly to accommodate between 600 to 800 ml of urine at maximum capacity. transitional epithelium, elastic fibers, and visceral muscle tissue in the walls of the. Four parts make up the structure (anatomy) of the bladder: dome. the dome, or apex, is the top front part of your bladder. it points toward your abdominal wall. base. the base is the bottom back part of your bladder, also referred to as the fundus. body. the bladder body makes up the area between the dome and the base. neck. the bladder neck is.

Eventual Erosion Of The Bladder Wall Trialexhibits Inc The urinary bladder functions as a storage vessel for urine to delay the frequency of urination. it is one of the most elastic organs of the body and is able to increase its volume greatly to accommodate between 600 to 800 ml of urine at maximum capacity. transitional epithelium, elastic fibers, and visceral muscle tissue in the walls of the. Four parts make up the structure (anatomy) of the bladder: dome. the dome, or apex, is the top front part of your bladder. it points toward your abdominal wall. base. the base is the bottom back part of your bladder, also referred to as the fundus. body. the bladder body makes up the area between the dome and the base. neck. the bladder neck is. The urinary bladder is a pelvic organ that collects and holds urine before urination. it serves as a temporary reservoir for urine produced by the kidneys. when empty, it lies completely within the pelvic cavity, but enlarges upward into the abdominal cavity when full. it is the most anterior pelvic organ, located just behind the pubic bones. Anterior cut away view of the male urinary bladder, prostate and urethra with foley catheter in place, visualizing the postoperative condition of a scab formed over the tumor removal site and the subsequent bladder perforation.
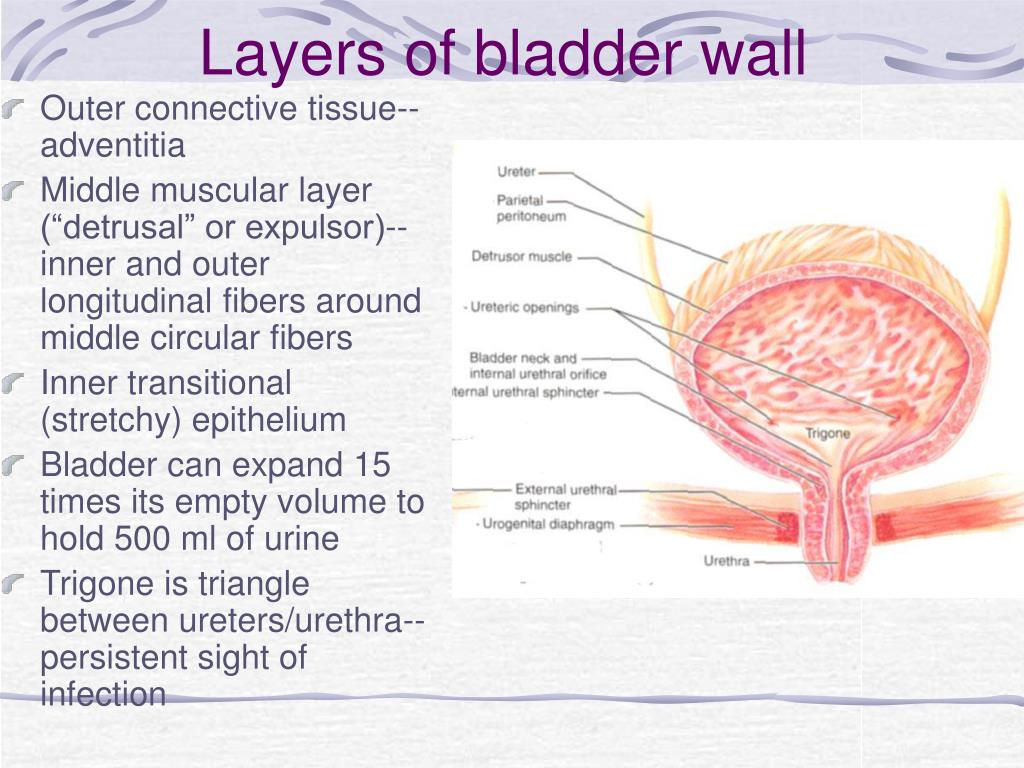
Bladder Wall Anatomy The urinary bladder is a pelvic organ that collects and holds urine before urination. it serves as a temporary reservoir for urine produced by the kidneys. when empty, it lies completely within the pelvic cavity, but enlarges upward into the abdominal cavity when full. it is the most anterior pelvic organ, located just behind the pubic bones. Anterior cut away view of the male urinary bladder, prostate and urethra with foley catheter in place, visualizing the postoperative condition of a scab formed over the tumor removal site and the subsequent bladder perforation.

Schematic Diagram Of The Bladder Wall And Bladder Permeability Barrier

Comments are closed.