Alpha Decay And Conservation Laws

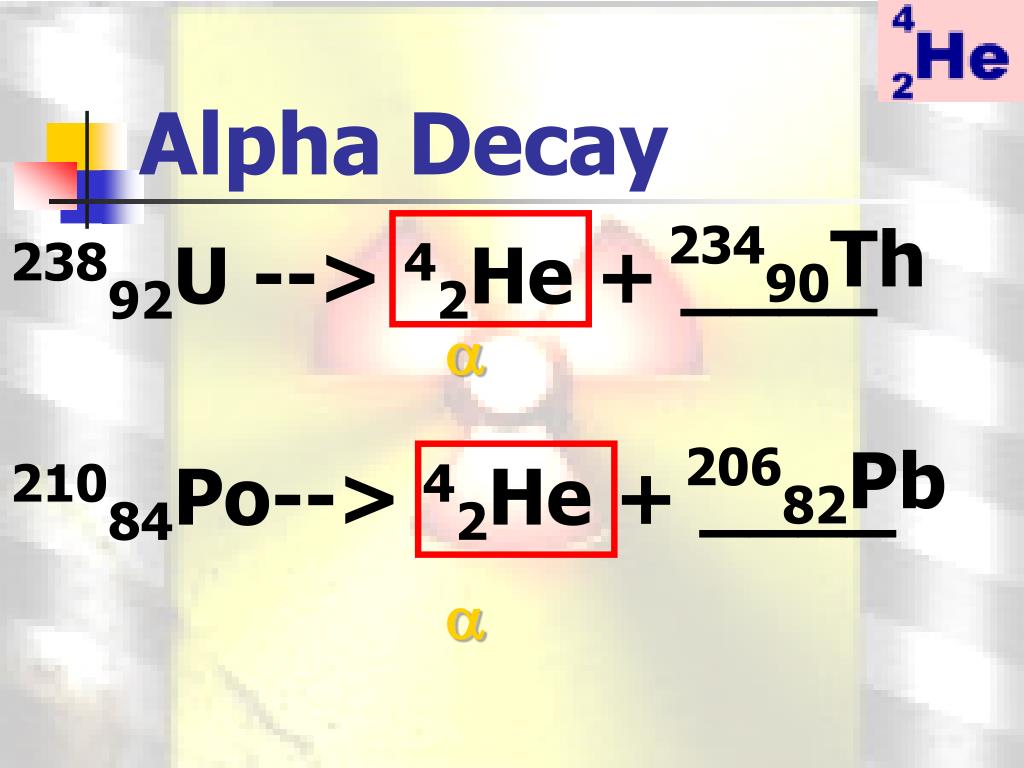
Alpha Decay And Conservation Laws Youtube Define and discuss nuclear decay. state the conservation laws. explain parent and daughter nucleus. calculate the energy emitted during nuclear decay. nuclear decay has provided an amazing window into the realm of the very small. nuclear decay gave the first indication of the connection between mass and energy, and it revealed the existence of. There are three major types of nuclear decay, called alpha (α) beta (β) and gamma (γ). the α decay equation is a zxn →a − 4 z − 2yn − 2 4 2he2. nuclear decay releases an amount of energy e related to the mass destroyed Δm by e = (Δm)c2. there are three forms of beta decay.

A Guide To Alpha Decay Including Equations And Uses Science Drill As discussed in atomic physics, the general relationship is e = (∆ m) c2. here, e is the nuclear reaction energy (the reaction can be nuclear decay or any other reaction), and Δ m is the difference in mass between initial and final products. when the final products have less total mass, Δ m is positive, and the reaction releases energy (is. When a parent nucleus decays, it produces a daughter nucleus following rules and conservation laws. there are three major types of nuclear decay, called alpha (), beta (), and gamma (). the decay equation is. nuclear decay releases an amount of energy related to the mass destroyed by. there are three forms of beta decay. Rate of decay is characterized by half life, the time it takes for half of a radioactive sample to decay; conservation laws in nuclear reactions. conservation of mass energy: total mass energy of closed system remains constant during nuclear reactions mass can be converted into energy and vice versa (e = m c 2 e=mc^2 e = m c 2). When a parent nucleus decays, it produces a daughter nucleus following rules and conservation laws. there are three major types of nuclear decay, called alpha (), beta (), and gamma (). the decay equation is. nuclear decay releases an amount of energy related to the mass destroyed by. there are three forms of beta decay.
Ppt Nuclear Chemistry Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5889735 Rate of decay is characterized by half life, the time it takes for half of a radioactive sample to decay; conservation laws in nuclear reactions. conservation of mass energy: total mass energy of closed system remains constant during nuclear reactions mass can be converted into energy and vice versa (e = m c 2 e=mc^2 e = m c 2). When a parent nucleus decays, it produces a daughter nucleus following rules and conservation laws. there are three major types of nuclear decay, called alpha (), beta (), and gamma (). the decay equation is. nuclear decay releases an amount of energy related to the mass destroyed by. there are three forms of beta decay. Alpha decay is the separation of a [latex]{}^{4}\text{he}[ latex] nucleus from the parent. the daughter nucleus has two fewer protons and two fewer neutrons than the parent. alpha decay occurs spontaneously only if the daughter and [latex]{}^{4}\text{he}[ latex] nucleus have less total mass than the parent. Alpha decay (or α decay and alpha radioactivity) represents the disintegration of a parent nucleus to a daughter through the emission of the nucleus of a helium atom. alpha decay is a quantum tunneling process. to be emitted, the alpha particle must penetrate a potential barrier. this transition can be characterized as:.

Nuclear Decay And Conservation Laws в Physics Alpha decay is the separation of a [latex]{}^{4}\text{he}[ latex] nucleus from the parent. the daughter nucleus has two fewer protons and two fewer neutrons than the parent. alpha decay occurs spontaneously only if the daughter and [latex]{}^{4}\text{he}[ latex] nucleus have less total mass than the parent. Alpha decay (or α decay and alpha radioactivity) represents the disintegration of a parent nucleus to a daughter through the emission of the nucleus of a helium atom. alpha decay is a quantum tunneling process. to be emitted, the alpha particle must penetrate a potential barrier. this transition can be characterized as:.

Comments are closed.