A B Sagittal And Transverse Ultrasound Sections Of The Pelvis A
A B Sagittal And Transverse Ultrasound Sections Of The Pelvis A Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the axial plane divides the body into what sections? a.left and right b.posterior and anterior c.front and back d.superior and inferior, what position is the body placed in when it is in an oblique position? a.lying on the back, face up b.lying down, face down c.at an angle, neither frontal nor lateral d.lying on the side, what x. The probe is then moved in this orientation through the uterus and adnexa laterally out to each sidewall to image the entire pelvis in the longitudinal plane. b, urinary bladder; r, rectum; u, uterus. b, corresponding transvaginal sonogram in the sagittal plane demonstrating the corpus of the uterus as depicted in a. bo, bowel.

A B Sagittal And Transverse Ultrasound Sections Of The Pelvis A Uterus trans abdominal (ta) approach probe positioning for longitudinal scan. the heel of the probe should be at symphysis pubis. angle the probe slightly towards the heard to have the ultrasound beam perpendicular to the uterus. ultrasound of uterus sagittal, transabdominal approach, ultrasound image image. Keywords. ultrasound imaging has shown an extremely rapid evolution in the last two decades, thanks to the development of highly sophisticated both two dimensional (2d) and three dimensional (3d) technology and blood flow mapping, which render ultrasound the first line imaging modality for the evaluation of the female pelvis. the interpretation. Download scientific diagram | (a, b) sagittal and transverse ultrasound sections of the pelvis. a fluid filled cystic lesion in the midline of the pelvis (arrow) in continuity with the cervix. Abstract. ultrasound imaging has shown an extremely rapid evolution in the last two decades, thanks to the development of highly sophisticated both two dimensional (2d) and three dimensional (3d) technology and blood flow mapping, which render ultrasound the first line imaging modality for the evaluation of the female pelvis.

A Sagittal And B Transverse Pelvic Ultrasound Images Showing A Download scientific diagram | (a, b) sagittal and transverse ultrasound sections of the pelvis. a fluid filled cystic lesion in the midline of the pelvis (arrow) in continuity with the cervix. Abstract. ultrasound imaging has shown an extremely rapid evolution in the last two decades, thanks to the development of highly sophisticated both two dimensional (2d) and three dimensional (3d) technology and blood flow mapping, which render ultrasound the first line imaging modality for the evaluation of the female pelvis. Ultrasound transducer sends sound waves through the body. sound waves are reflected differently by various types of tissue, and sent back to transducer where signal is transformed into visible image. sound waves travel through soft tissue or fluid. these types of structures are used as “windows” for us scanning. A, sagittal and b, transverse pelvic ultrasound images showing a tortuous fallopian tube (solid black arrow) tapering superiorly at the cornu of a normal uterus (solid white arrow) with normal.
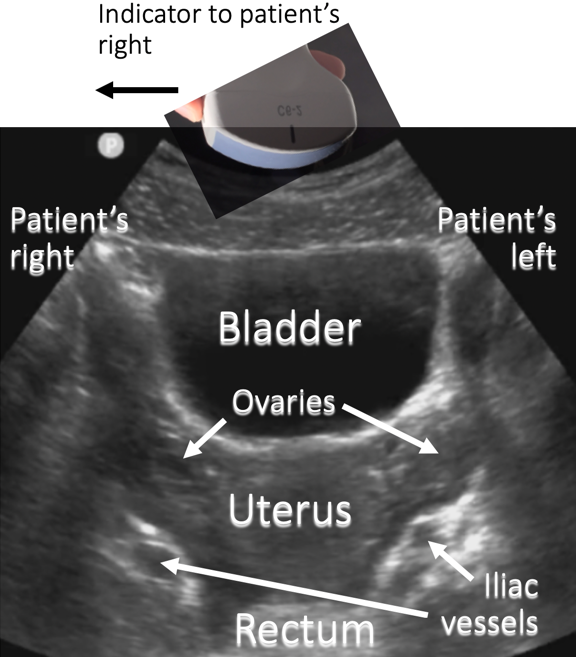
Pelvic Ultrasound Transverse Anatomy Ultrasound transducer sends sound waves through the body. sound waves are reflected differently by various types of tissue, and sent back to transducer where signal is transformed into visible image. sound waves travel through soft tissue or fluid. these types of structures are used as “windows” for us scanning. A, sagittal and b, transverse pelvic ultrasound images showing a tortuous fallopian tube (solid black arrow) tapering superiorly at the cornu of a normal uterus (solid white arrow) with normal.

Comments are closed.