5 Types Of Consumers Biology
Ppt Chapter 36 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5568372 Examples of primary consumers are zooplankton, butterflies, rabbits, giraffes, pandas and elephants. primary consumers are herbivores. their food source is the first trophic level of organisms within the food web, or plants. plants are also referred to as autotrophs. Learn about the different types of consumers in ecosystems, from primary producers to tertiary carnivores. find out how they interact with each other and with decomposers in a trophic pyramid.

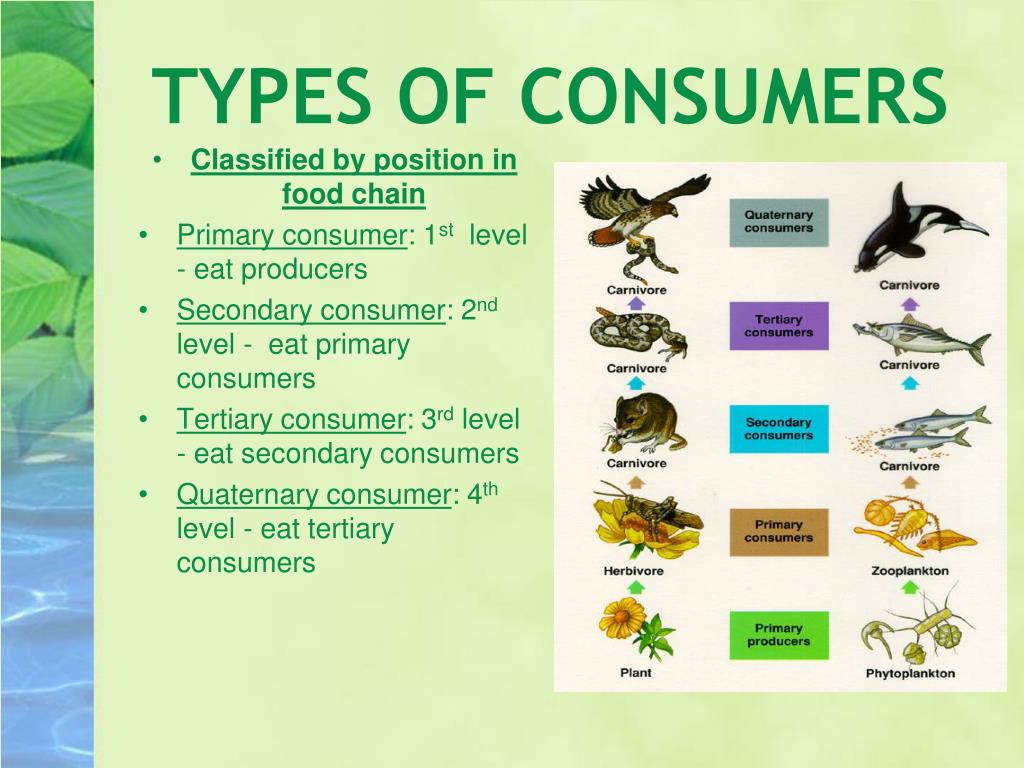
Ppt Chapter 13 Principles Of Ecology Powerpoint Presentation Free Learn the consumer definition in biology with examples. see the different classifications of consumers in an ecosystem. updated: 11 21 2023 there are four main types of consumers:. The producer definition in biology is an organism that makes its own food. an organism is any living thing, whether plant, animal, bacteria, fungi, etc. while plants are definitely producers. A consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. a consumer is a heterotroph and a producer is an autotroph. like sea angels, they take in organic moles by consuming other organisms, so they are commonly called consumers. heterotrophs can be classified by what they usually eat as herbivores. Organisms that manufacture their own food are known as producers or autotrophs. energy from the sun or chemicals is one of the major ingredients of this food. with the help of water, producers convert this energy into sugar or food, which are usable forms of energy. producers are largely green plants, which use sunlight and water to generate.

Consumer Biology Britannica A consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. a consumer is a heterotroph and a producer is an autotroph. like sea angels, they take in organic moles by consuming other organisms, so they are commonly called consumers. heterotrophs can be classified by what they usually eat as herbivores. Organisms that manufacture their own food are known as producers or autotrophs. energy from the sun or chemicals is one of the major ingredients of this food. with the help of water, producers convert this energy into sugar or food, which are usable forms of energy. producers are largely green plants, which use sunlight and water to generate. A primary consumer eats producers (e.g., a caterpillar eating a leaf); a secondary consumer eats primary consumers (e.g., a robin eating the caterpillar). and it can go even further: a tertiary consumer eats secondary consumers (e.g., a hawk eating the robin). a single individual animal can act as a different type of consumer depending on what. Producers are organisms that produce food for themselves and other organisms. they use energy and simple inorganic molecules to make organic compounds. the stability of producers is vital to ecosystems because all organisms need organic molecules. producers are also called autotrophs. there are two basic types of autotrophs: photoautotrophs and.

Comments are closed.