2 1 Basic Concept Crystal Structure Lattice Structure Basis Lattice Points Positio
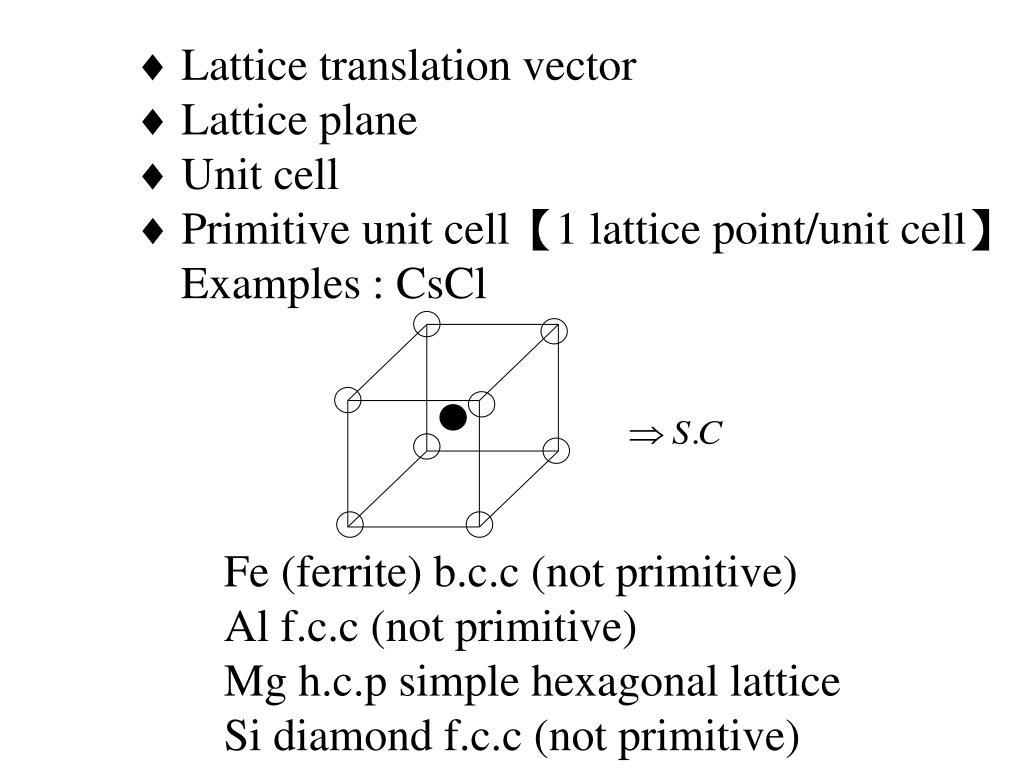
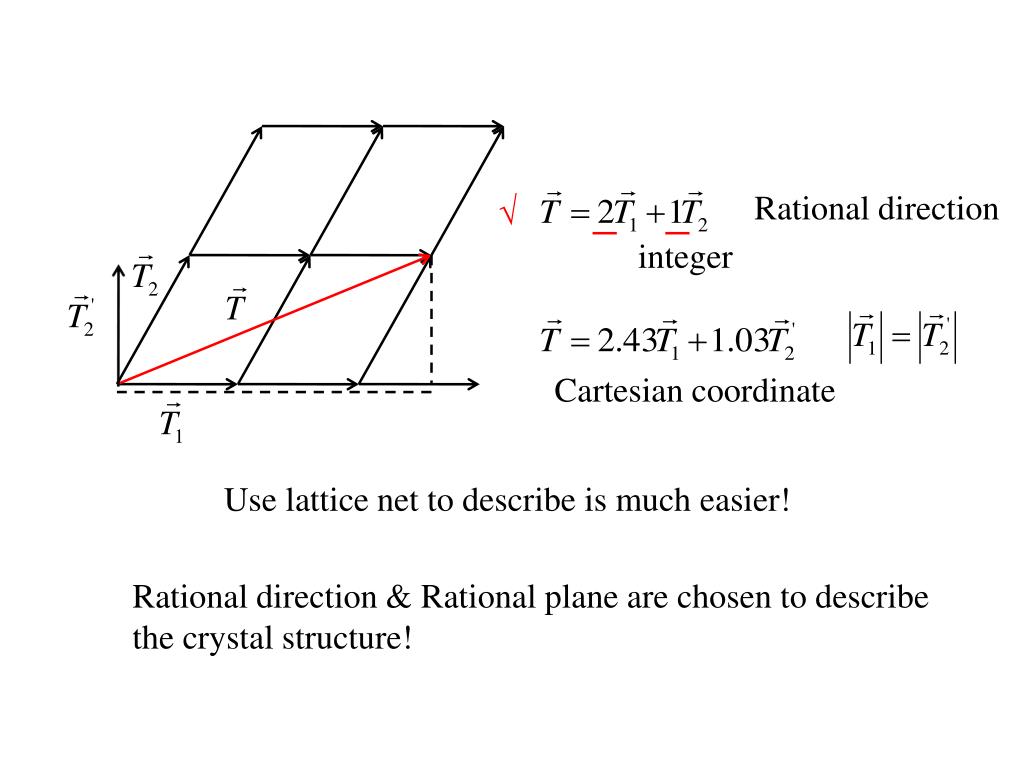
Ppt 2 1 Basic Concept Crystal Structure Lattice Structu 3.1 some basic concepts of crystal structure: basis and lattice. r = n1a n2b n3c. such a lattice is called a bravais lattice. the translational vectors, a, b, and c are the primitive vectors. note that the choice for the set of primitive vectors for any given bravais lattice is not unique. there are three common cubic bravais lattices. α β 1. lattice vectors connect γ ~ b two lattice points. 2. any lattice point may be reached from any other. ~ a by the vector addition of an integral number of. in general, the lattice vectors do not need to be lattice vectors. the same length, nor do they need to be normal 3. non integral combinations to each other.
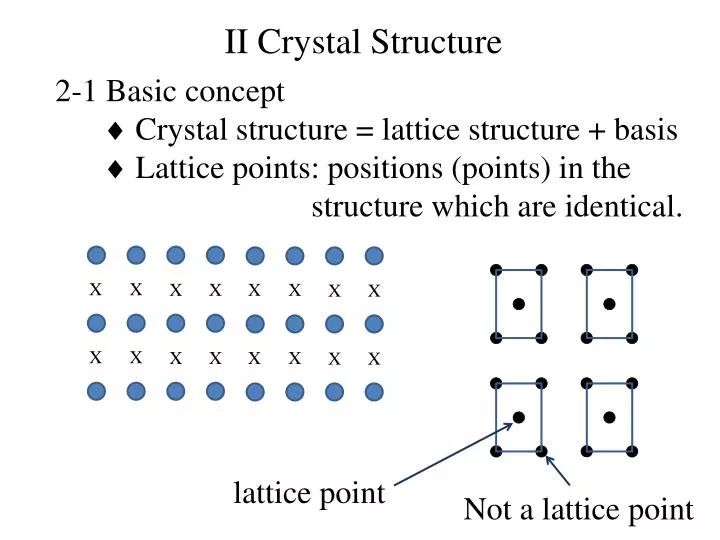
Ppt 2 1 Basic Concept Crystal Structure Lattice Structu Basis and crystal. now one could go ahead and replace the lattice points by more complex objects (called basis), e.g. a group of atoms, a molecule, . this generates a structure that is referred to as a crystal: [11][12][13][14] a crystal is defined as a lattice with a basis added to each lattice site. usually the basis consists of an atom. Crystal structure = lattice basis. the lattice is defined by fundamental translation vectors. for example, the position vector of any lattice site of the two dimensional lattice in fig.3 can be written as t=n1a1 n2a2 , (1.1) where a1 and a2 are the two vectors shown in fig.3, and n1,n2 is a pair of integers whose values depend on the lattice. 2. crystal structure: (a) definitions — explain the terms basis and crystal structure, and how the lattice and basis together form the crystal structure. given the crystal structure, is the choice of lattice and basis unique? (b) examples — i. give and draw a lattice and basis that together describe the cscl crystal structure. ii. Figure 10.6.10: a unit cell is defined by the lengths of its three axes ( a, b, and c) and the angles ( α, β, and γ) between the axes. there are seven different lattice systems, some of which have more than one type of lattice, for a total of fourteen different unit cells, which have the shapes shown in figure 10.6.11.
Ppt 2 1 Basic Concept Crystal Structure Lattice Structu 2. crystal structure: (a) definitions — explain the terms basis and crystal structure, and how the lattice and basis together form the crystal structure. given the crystal structure, is the choice of lattice and basis unique? (b) examples — i. give and draw a lattice and basis that together describe the cscl crystal structure. ii. Figure 10.6.10: a unit cell is defined by the lengths of its three axes ( a, b, and c) and the angles ( α, β, and γ) between the axes. there are seven different lattice systems, some of which have more than one type of lattice, for a total of fourteen different unit cells, which have the shapes shown in figure 10.6.11. A1. definition: primitive unit cell = a region in space, when translated using all lattice vectors r, fills neatly the whole space (w o overlapping regions or voids) 2d examples: 2 possible choices out of . 3d example: (obvious choice) theorem: volume of primitive cell a a. 1 2 a ; v = volume of crystal, 3. Defining basis: basis is whatever we put physically at the abstract lattice points – can be single atom ion or groups of them. each lattice point will have identical basis – this makes up the crystal structure. lattice basis = crystal structure. co ordination number: number of nearest neighbours in a lattice.
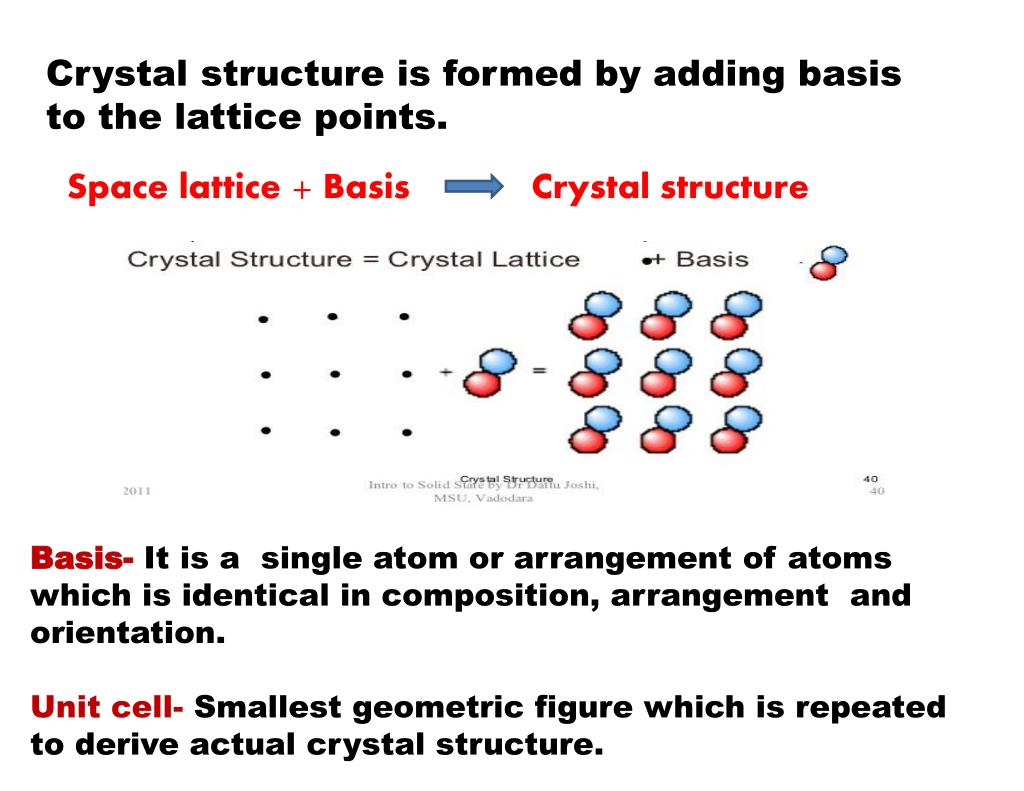
Ppt Crystal Physics Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 4024329 A1. definition: primitive unit cell = a region in space, when translated using all lattice vectors r, fills neatly the whole space (w o overlapping regions or voids) 2d examples: 2 possible choices out of . 3d example: (obvious choice) theorem: volume of primitive cell a a. 1 2 a ; v = volume of crystal, 3. Defining basis: basis is whatever we put physically at the abstract lattice points – can be single atom ion or groups of them. each lattice point will have identical basis – this makes up the crystal structure. lattice basis = crystal structure. co ordination number: number of nearest neighbours in a lattice.
Ppt 2 1 Basic Concept Crystal Structure Lattice Structu

Comments are closed.