Ray Diagrams For Images Formed By Convex Concave Lenses

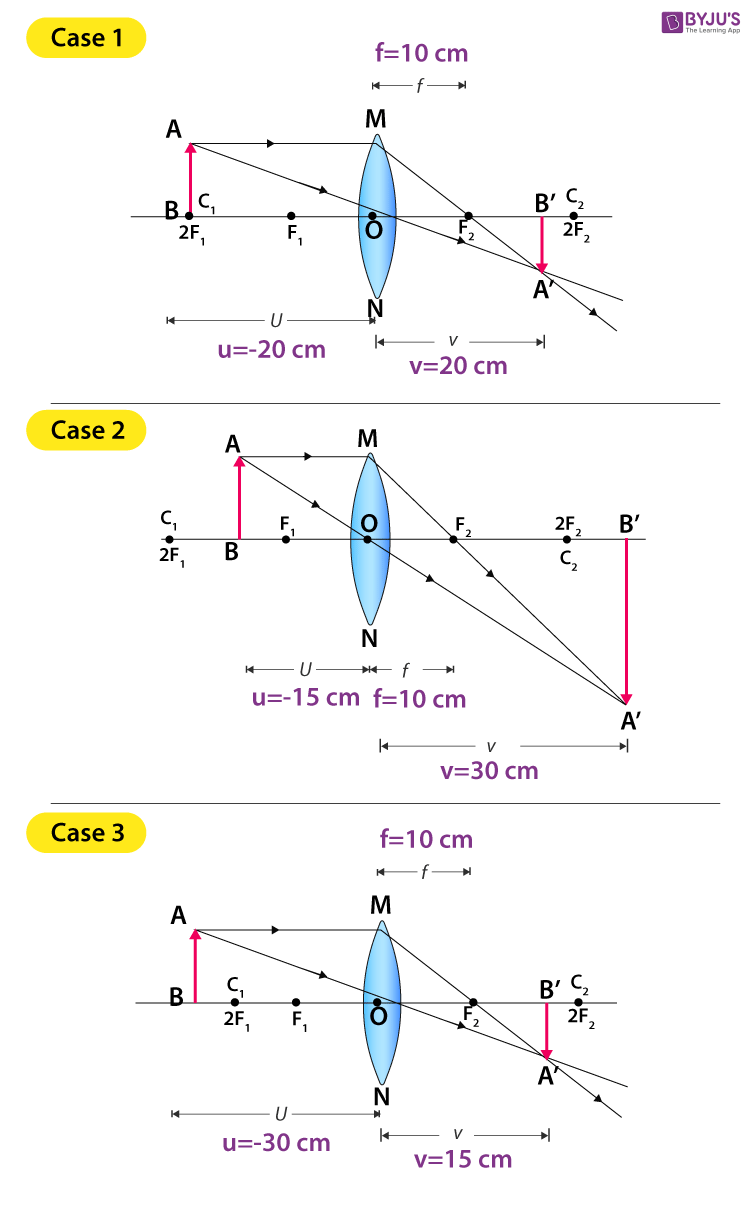
Ray Diagrams For Images Formed By Convex Concave Lenses Here in this post, you will get ray diagrams for images formed by convex & concave lenses as a quick reference. First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis. so, it passes through focus after refraction.

Ray Diagrams For Images Formed By Convex Concave Lenses In optics, a ray is a geometrical representation of the light that is idealized by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the wave fronts of actual light and points in the energy flow direction. It discusses the key terms including principal axis, focus, center of curvature and explains how to use ray diagrams to determine the location, orientation, size and type of images formed by concave and convex mirrors in different configurations. Master ray diagrams for converging lenses with our detailed step by step guide. perfect for physics students. The document provides instructions to complete ray diagrams in two tables to determine the characteristics of images formed by convex and concave lenses.

Solution Ray Diagrams Convex And Concave Lenses Studypool Master ray diagrams for converging lenses with our detailed step by step guide. perfect for physics students. The document provides instructions to complete ray diagrams in two tables to determine the characteristics of images formed by convex and concave lenses. Rules for convex lens : 1. light ray incident parallel to the principal axis , meet at focus. 2. light ray incident from focus , become parallel to the principal axis after refraction. 3. light ray incident on the pole of the lens passes without any deviation. Thus, the lenses that are formed after binding two spherical surfaces bulging outward are called convex lenses, whereas the lenses that are formed after binding two spherical surfaces so that they are curved inward are called concave lenses. For a concave lens, there are only 2 cases. they are. in this case, object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance) so, we draw rays parallel to principal axis. since ray parallel to principal axis appear to pass through the focus. all rays appear to meet at focus after refraction. hence, image is formed at focus. Reason 1 (62.1): ray diagrams illustrate how lenses form images by tracing the path of light rays. for a concave lens with the object between f and 2f, specific ray tracing rules determine the image location.

Solution Ray Diagrams Convex And Concave Lenses Studypool Rules for convex lens : 1. light ray incident parallel to the principal axis , meet at focus. 2. light ray incident from focus , become parallel to the principal axis after refraction. 3. light ray incident on the pole of the lens passes without any deviation. Thus, the lenses that are formed after binding two spherical surfaces bulging outward are called convex lenses, whereas the lenses that are formed after binding two spherical surfaces so that they are curved inward are called concave lenses. For a concave lens, there are only 2 cases. they are. in this case, object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance) so, we draw rays parallel to principal axis. since ray parallel to principal axis appear to pass through the focus. all rays appear to meet at focus after refraction. hence, image is formed at focus. Reason 1 (62.1): ray diagrams illustrate how lenses form images by tracing the path of light rays. for a concave lens with the object between f and 2f, specific ray tracing rules determine the image location.

Solution Ray Diagrams Of Convex And Concave Lenses Studypool For a concave lens, there are only 2 cases. they are. in this case, object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance) so, we draw rays parallel to principal axis. since ray parallel to principal axis appear to pass through the focus. all rays appear to meet at focus after refraction. hence, image is formed at focus. Reason 1 (62.1): ray diagrams illustrate how lenses form images by tracing the path of light rays. for a concave lens with the object between f and 2f, specific ray tracing rules determine the image location.
Convex Lenses And Ray Diagrams Examples Solutions
Comments are closed.